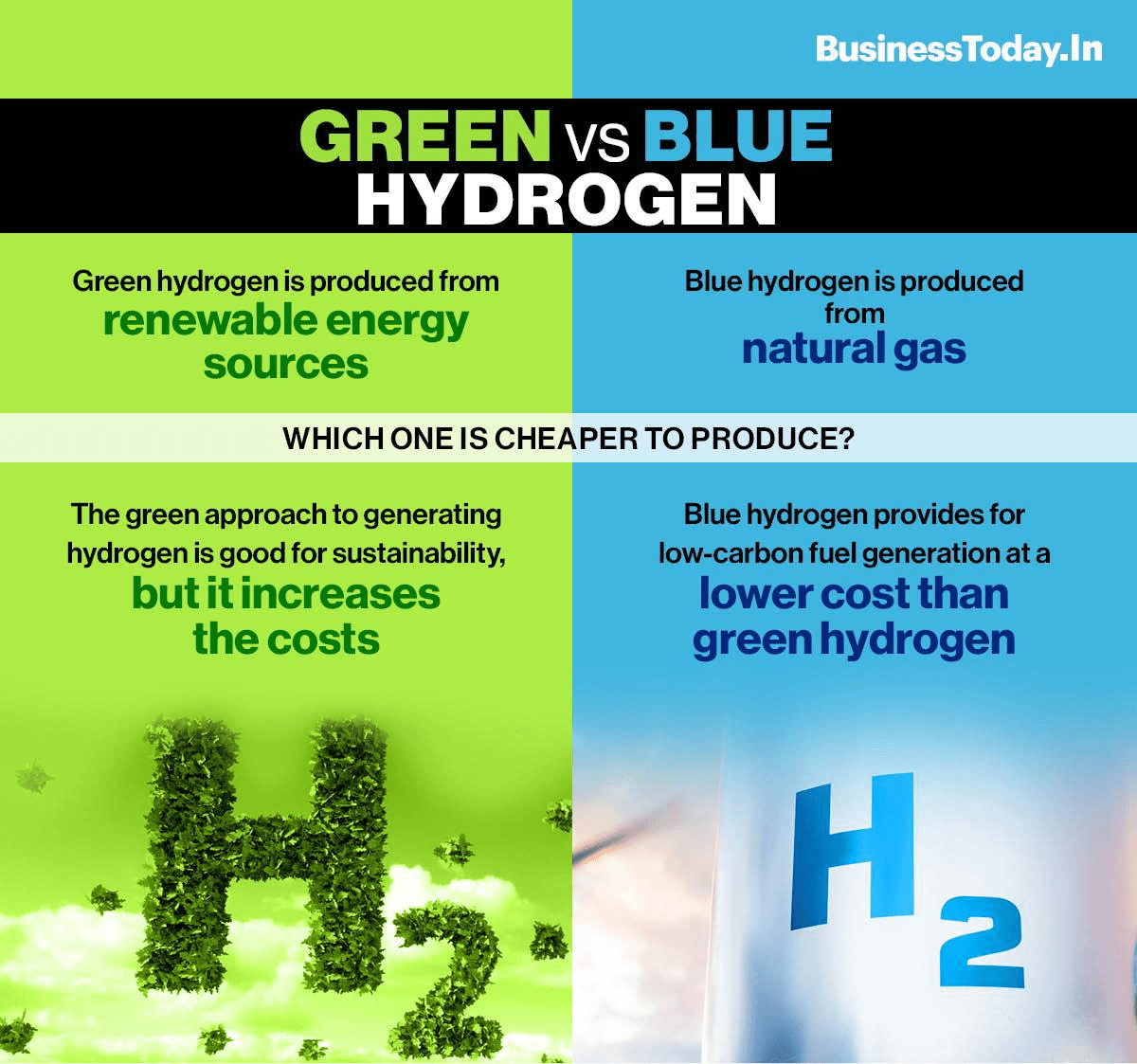
Nel and Samsung C&T have partnered to convert excess nuclear energy into hydrogen, introducing the concept of “pink hydrogen.” Utilizing Nel’s advanced alkaline electrolyzers, the project aims to optimize energy efficiency and reduce carbon emissions. This initiative not only showcases technological innovation but also serves as a global model for using hydrogen as a clean energy vector, particularly in decarbonizing energy-intensive industries. With a €135 million grant from the EU Innovation Fund, Nel is accelerating the industrialization of next-generation electrolyzer technology, further solidifying hydrogen’s role in sustainable energy systems.