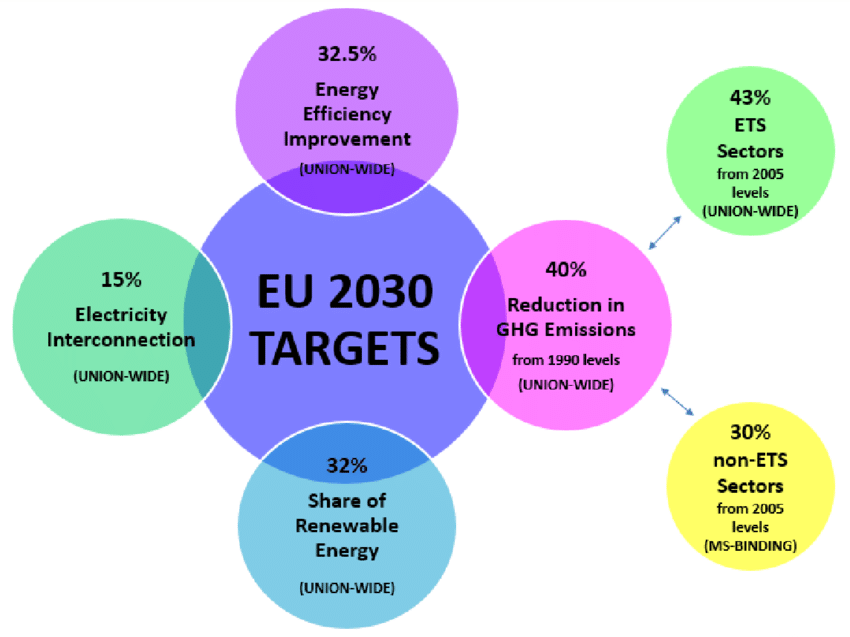
In 2023, the European Union (EU) achieved a significant milestone by reaching a record high of 24.5% in renewable energy use[1]. This progress, while commendable, still falls short of the ambitious 2030 target of 42.5%. The journey towards this goal is marked by varying degrees of success among member states, highlighting both the achievements and the challenges that lie ahead.
Leading the Way: Sweden, Finland, and Denmark
Sweden stands out as the leader in renewable energy adoption within the EU, boasting the highest share of renewable energy. This success is mirrored by Finland and Denmark, both of which have made substantial strides in integrating renewable sources into their energy mix. These countries serve as exemplary models, demonstrating the potential for significant progress when there is strong policy support and investment in renewable technologies.
In Sweden, the government’s commitment to sustainability is evident through comprehensive policies and incentives that encourage both public and private sectors to invest in renewable energy projects. The country has leveraged its natural resources, such as abundant wind and hydro power, to create a robust renewable energy infrastructure. Sweden’s success is also attributed to its innovative approach to energy storage and grid management, ensuring a stable and reliable supply of renewable energy.
Similarly, Finland has made remarkable advancements by focusing on bioenergy and wind power. The Finnish government has implemented strategic plans to reduce carbon emissions and increase the share of renewables in the national energy mix. Finland’s emphasis on research and development has led to significant technological advancements, making renewable energy more efficient and cost-effective.
Denmark, known for its pioneering wind energy sector, has set ambitious targets to become carbon neutral by 2050. The Danish government has fostered a collaborative environment where public-private partnerships thrive, driving large-scale renewable energy projects. Denmark’s success is also due to its proactive community engagement, where local communities are involved in renewable energy initiatives, fostering widespread support and participation.
These countries exemplify how a combination of strong policy frameworks, substantial investments, and community involvement can lead to significant advancements in renewable energy adoption. Their achievements provide valuable lessons for other EU member states striving to meet their renewable energy targets.
Growth Rates: A Decade of Progress
Over the past decade, Denmark, Sweden, and Estonia have experienced the fastest growth rates in renewable energy use[1]. This rapid expansion is a testament to their commitment to sustainable energy practices and their proactive approach to addressing climate change. The success of these countries underscores the importance of consistent policy frameworks, financial incentives, and public support in driving the transition to renewable energy.
In Denmark, Sweden, and Estonia, the rapid growth in renewable energy use is driven by a combination of forward-thinking policies and substantial investments in green technologies. These countries have implemented comprehensive strategies that include subsidies for renewable energy projects, tax incentives for clean energy investments, and stringent regulations to reduce carbon emissions.
Public support has also played a crucial role. In Denmark, for example, community-owned wind farms have become a popular model, allowing local residents to invest in and benefit from renewable energy projects. This not only boosts public acceptance but also ensures that the economic benefits of renewable energy are widely shared.
Financial incentives have been pivotal in making renewable energy projects economically viable. Governments in these countries have provided grants and low-interest loans to support the development of renewable energy infrastructure. This financial backing has encouraged private sector investment and innovation, leading to advancements in technology and reductions in the cost of renewable energy.
Moreover, these countries have prioritized education and awareness campaigns to inform the public about the benefits of renewable energy and the importance of sustainability. By fostering a culture of environmental responsibility, they have garnered widespread support for their renewable energy initiatives.
The proactive approach of Denmark, Sweden, and Estonia serves as a powerful example of how a combination of strong policy frameworks, financial incentives, and public support can drive significant progress in renewable energy adoption. Their success highlights the critical role of government leadership and community engagement in achieving sustainable energy goals.
Lagging Behind: Croatia, Romania, and North Macedonia
In contrast, Croatia, Romania, and North Macedonia have reported the lowest growth rates in renewable energy adoption[1]. These countries face unique challenges, including economic constraints, limited infrastructure, and varying levels of political commitment. Addressing these barriers is crucial for ensuring that all EU member states can contribute to and benefit from the collective goal of increased renewable energy use.
The Gap to Target: Accelerating Progress
To meet the 2030 target, the EU needs an annual growth rate of 2.6% in renewable energy use[1]. However, the average growth rate over the past decade has been only 0.79%[1]. This discrepancy highlights the need for accelerated efforts and innovative solutions to bridge the gap. The EU must enhance its strategies, focusing on areas such as technological innovation, cross-border cooperation, and increased funding for renewable energy projects.
Ecological and Sustainability Implications
The transition to renewable energy is not just about meeting targets; it has profound ecological and sustainability implications. Renewable energy sources, such as wind, solar, and hydro, offer cleaner alternatives to fossil fuels, reducing greenhouse gas emissions and mitigating climate change. The widespread adoption of these technologies can lead to improved air quality, preservation of natural habitats, and a reduction in the ecological footprint of energy production.
Consequences of Falling Short
Failing to meet the 2030 renewable energy targets could have significant consequences. Continued reliance on fossil fuels would exacerbate climate change, leading to more severe weather events, rising sea levels, and loss of biodiversity. Economically, it could result in higher energy costs and increased dependence on energy imports, undermining the EU’s energy security and economic stability.
Potential Solutions and Strategies
To overcome these challenges, the EU can adopt several strategies:
- Enhanced Policy Measures: Strengthening policy frameworks to provide clear, long-term signals to investors and stakeholders is crucial. This includes setting ambitious but achievable targets, offering financial incentives, and removing regulatory barriers.
- Investment in Technology: Investing in research and development of advanced renewable energy technologies can drive innovation and reduce costs. This includes exploring new materials for solar panels, improving wind turbine efficiency, and developing energy storage solutions.
- Public-Private Partnerships: Encouraging collaboration between the public and private sectors can mobilize resources and expertise. Public-private partnerships can facilitate large-scale renewable energy projects, leveraging the strengths of both sectors.
- Education and Awareness: Raising public awareness about the benefits of renewable energy and the importance of sustainability can foster community support and participation. Educational campaigns can highlight the environmental, economic, and social advantages of transitioning to renewable energy.
- Regional Cooperation: Promoting regional cooperation and knowledge sharing among EU member states can enhance collective efforts. Countries can learn from each other’s successes and challenges, adopting best practices and innovative solutions.
- Financial Support: Increasing financial support for renewable energy projects, particularly in countries with lower growth rates, can help overcome economic barriers. This includes grants, low-interest loans, and subsidies for renewable energy installations.
Conclusion
The EU has made significant progress in increasing renewable energy use, but substantial efforts are still needed to achieve the 2030 targets. By adopting a comprehensive and collaborative approach, the EU can accelerate its transition to a sustainable energy future. This journey not only addresses the pressing issue of climate change but also paves the way for a more resilient, secure, and prosperous Europe.
Related Content
- A Comprehensive Look at Two Innovative Renewable Energy Projects: Solar Highways and the Western Green Energy Hub
- European Renewable Energy Companies Fleeing Vietnam: Challenges and Solutions for a Sustainable Future
- Floating Solar Power Plants: A New Horizon for Renewable Energy in Extreme Marine Conditions
- Cheapest and Most Expensive Countries for EV Charging in Europe: Understanding the Challenges and Opportunities for Renewable Energy
- Solar Farms as Habitats: A Dual Approach to Renewable Energy and Biodiversity
- The Future of Renewable Energy: Innovations and Challenges
- Renewables account for 24.5% of EU energy use in 2023
- Shedding light on energy in the EU – 2023 edition
- Renewables 2023: Analysis and forecast to 2028
References
[1] Renewables account for 24.5% of EU energy use in 2023