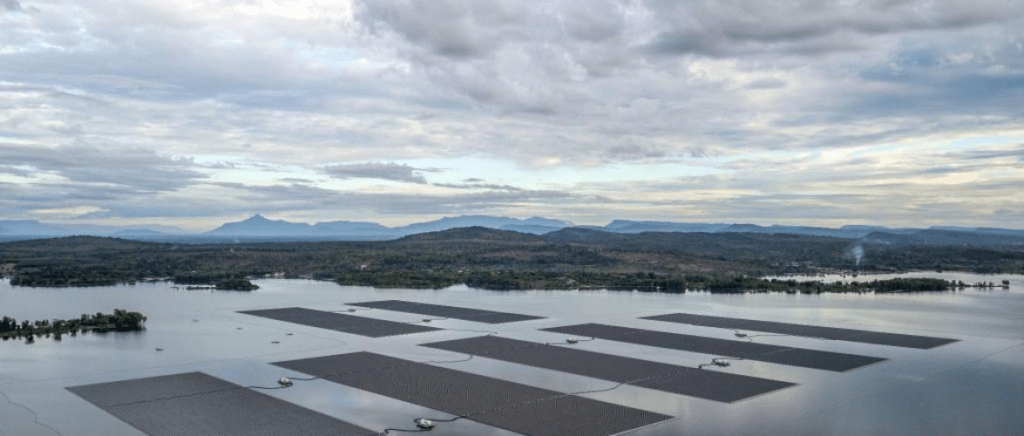
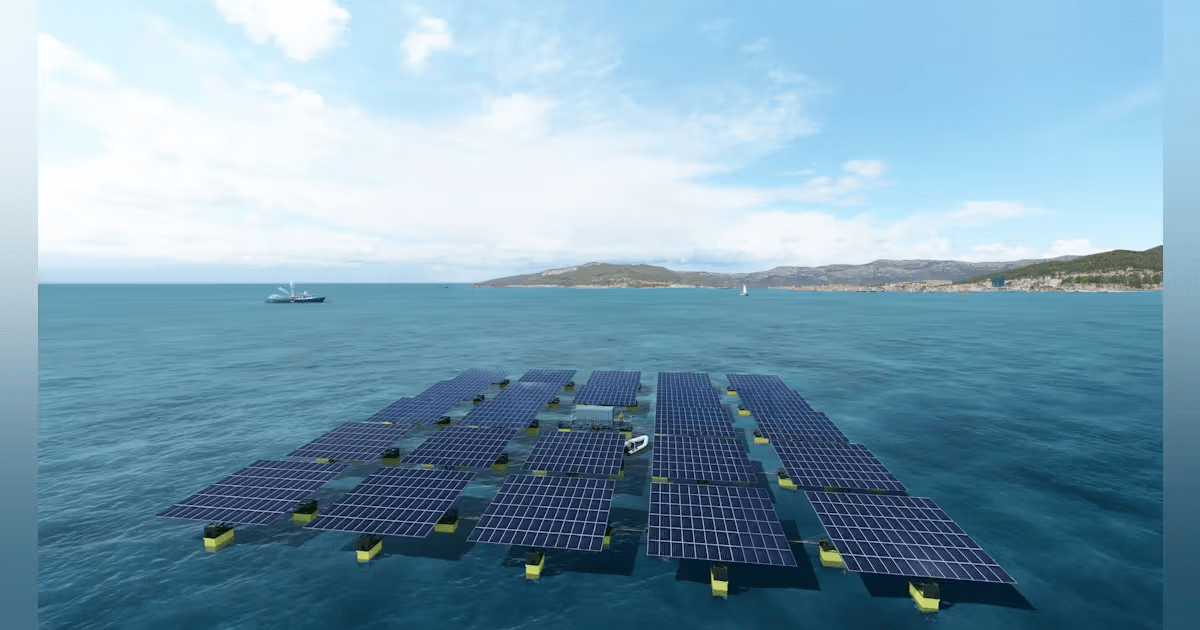
As the world grapples with the effects of climate change and increasing energy demand, innovative solutions are emerging to harness clean energy in novel ways. One such innovation comes from Saipem, an Italian startup, with the development of XolarSurf, a floating solar power plant designed to operate in extreme marine conditions. This technology presents the potential to revolutionize how we approach energy production, particularly in regions where land space is limited or where the climate makes traditional solar farms difficult to implement.
XolarSurf is not only a response to the urgent need to transition from fossil fuels but also a solution for coastal and island communities facing energy scarcity. With the ability to produce 35-45 kWp of installed power per floating unit, this modular platform can help reduce dependence on non-renewable energy sources while contributing to a sustainable future. However, as promising as this innovation is, it also brings with it a set of challenges that need to be carefully addressed to ensure its long-term viability and minimal impact on the environment.
The Advantages of Floating Solar Technology
A Renewable Energy Source for Difficult Conditions
One of the most significant advantages of floating solar power plants is their ability to operate in environments where land-based solar farms are impractical. Coastal areas, island nations, and regions with limited land availability, such as densely populated cities, can benefit from these floating platforms. In addition, XolarSurf’s ability to function in extreme marine conditions—harsh weather, high waves, and salinity—gives it a unique edge over other renewable technologies, allowing energy production in places previously considered unsuitable.
By utilizing the vast surface area of the world’s oceans, these floating solar platforms offer a solution to the global energy crisis, providing a sustainable source of power that can be deployed almost anywhere. This adaptability can be a game-changer for regions heavily reliant on imported fossil fuels, offering the opportunity to become energy independent.
Integration with Other Renewable Energy Sources
Floating solar plants like XolarSurf can also be integrated into hybrid energy projects. For example, offshore wind farms, already established in many parts of the world, could be combined with floating solar installations to create more efficient and resilient energy systems. This hybrid approach maximizes energy production by utilizing both solar and wind resources, ensuring a more consistent energy supply throughout the day and across different weather conditions. In doing so, these hybrid platforms could significantly reduce the environmental footprint of energy production and help mitigate the unpredictable nature of renewable energy generation.
Lowering Greenhouse Gas Emissions
At its core, the greatest benefit of floating solar technology is its ability to provide a renewable energy source that helps reduce the world’s dependence on fossil fuels. By harnessing the power of the sun, XolarSurf can play a significant role in cutting greenhouse gas emissions, thereby contributing to global climate goals. In the long run, the widespread adoption of floating solar platforms could help slow the progression of climate change and protect vulnerable ecosystems from the devastating effects of rising temperatures.
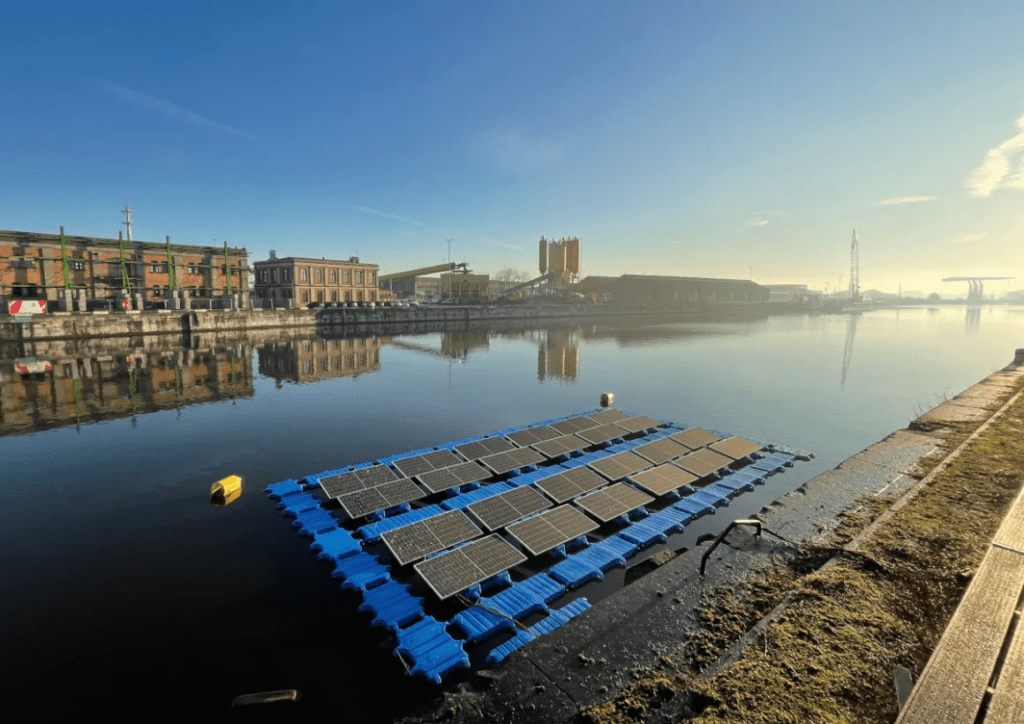

Challenges Facing Floating Solar Power Plants
While the promise of floating solar power is undeniable, several challenges need to be overcome to ensure its widespread adoption. These hurdles are not insurmountable, but addressing them requires concerted effort from governments, businesses, and the scientific community.
High Initial Costs
One of the most significant barriers to floating solar power is the high initial cost of developing and installing the technology. The materials used to construct these floating platforms must be durable and capable of withstanding the harsh conditions of the ocean, leading to higher upfront investment compared to traditional land-based solar installations. Furthermore, specialized equipment is often required to anchor these platforms securely to the seabed, adding another layer of expense.
Governments and financial institutions could play a crucial role in overcoming this challenge by offering incentives, grants, and subsidies for renewable energy projects. Reducing the financial burden on developers would encourage greater investment in floating solar technology and accelerate its adoption. Moreover, as the technology matures and scales up, the cost of production is expected to decrease, making it more accessible over time.
Maintenance in Extreme Conditions
Operating in marine environments poses unique maintenance challenges for floating solar power plants. Saltwater corrosion, storm damage, and marine life interference are all potential threats to the longevity of these installations. The platforms will need regular maintenance and monitoring to ensure that they remain operational and efficient over time.
Advancements in materials science and engineering could help mitigate some of these issues. For example, the development of corrosion-resistant materials and improved anchoring systems will be essential to ensuring the durability and reliability of floating solar plants. Additionally, remote monitoring technologies, such as drones and AI-driven sensors, could help reduce the need for manual inspections and maintenance, thereby lowering operational costs.
Environmental Impact on Marine Ecosystems
While floating solar platforms offer environmental benefits by reducing carbon emissions, they could also have unintended consequences on marine ecosystems. The installation of large floating structures could disrupt marine habitats, affecting everything from fish populations to coral reefs. Additionally, the shading caused by solar panels could alter the natural balance of light and temperature in the water below, potentially impacting photosynthetic marine organisms.
To address these concerns, careful environmental impact assessments will need to be conducted before the deployment of floating solar installations. These assessments should focus on understanding how the platforms affect local ecosystems and identifying ways to minimize any negative effects. One potential solution is the development of eco-friendly designs that promote biodiversity, such as floating structures that serve as artificial reefs, providing habitats for marine life.
Concrete Solutions for Humankind
Government and Private Sector Collaboration
Collaboration between governments and the private sector will be key to overcoming the financial and technical challenges facing floating solar power plants. Governments can provide financial incentives, streamline permitting processes, and create policies that promote the adoption of renewable energy technologies. Meanwhile, the private sector can drive innovation, developing more efficient and cost-effective floating solar platforms that can withstand the rigors of the marine environment.
Countries that invest in floating solar technology will not only contribute to global climate goals but also position themselves as leaders in the burgeoning renewable energy market. This leadership could bring significant economic benefits, including job creation, technological development, and energy independence.
Encouraging Public-Private Partnerships for Hybrid Energy Systems
One practical way to scale up floating solar projects is by encouraging public-private partnerships for hybrid energy systems. Combining floating solar with offshore wind or wave energy projects creates a diversified renewable energy infrastructure, maximizing the use of ocean resources. Governments can offer incentives for hybrid projects, ensuring that companies have the financial backing to integrate multiple renewable energy sources.
International Cooperation for Global Deployment
Finally, international cooperation will be essential to the success of floating solar technology. Knowledge sharing between countries, particularly between developed and developing nations, will help to accelerate the global deployment of this technology. Countries that have already made significant progress in renewable energy can provide technical expertise and financial support to nations that are just beginning their transition.
This global cooperation will not only help reduce greenhouse gas emissions but also ensure that the benefits of renewable energy are shared equitably across the world.
Conclusion: A Step Toward a Sustainable Future
The development of floating solar power plants like XolarSurf represents a significant step forward in the transition to renewable energy. By providing a clean and adaptable energy source, these platforms have the potential to transform the way we produce electricity, particularly in areas where land-based solar farms are not feasible. However, to fully realize this potential, we must address the challenges of cost, maintenance, and environmental impact through collaboration, innovation, and careful planning.
With the right support, floating solar technology could become a cornerstone of a sustainable future, helping to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and protect our planet for future generations. The solutions we implement today will shape the world we leave behind, and floating solar power offers a bright path forward.
Related Content
- Marine Floating Solar Power: There is a future
- Solar Highways: A Bold Vision for a Greener Future
- Solar Panels on the Alps: Switzerland’s Bold Gamble with Nature
- The biggest project in history begins: 52 billion solar panels, and America covered
- Solar Farms as Habitats: A Dual Approach to Renewable Energy and Biodiversity
- IeGeek 2K Solar Security Camera Outdoor Wireless Wifi CCTV Camera System Alexa
- HEIYOUCAM 2-Pack Solar-Powered Security Cameras Wireless Outdoor
- 4G LTE EU Solar Security Camera with SIM Card Slot
- 1pc, Cat Scarer Solar Powered Cat Repellent Fox Repellent Garden Ultrasonic Pet Deterrents
- 1pc Solar Watering Bottle With String Light, Hanging Solar Waterfall Light
- 20000mAh Rechargeable Solar Powered Portable Fan With Led Lantern
- China building two-thirds of world’s wind and solar projects
- Floating solar power plants on the ocean
- DNV and Moss Maritime team up to propel floating solar