As the global conversation about climate change and sustainability intensifies, it becomes clear that different countries contribute to carbon emissions in varying degrees based on their economic development, industrial activities, and consumption patterns. However, the path to reducing carbon emissions and mitigating environmental degradation is not the same for every nation. This article looks at how consumption-based carbon emissions differ by country, highlights the global inequalities in environmental responsibilities, and explores potential solutions for each nation to reduce their carbon footprint and promote sustainability.
Understanding Consumption-Based Carbon Emissions
Consumption-based carbon emissions are those tied to the consumption of goods and services within a country, rather than where those goods and services are produced. This perspective allows us to see the environmental impact of a nation’s lifestyle and consumption habits, providing a more nuanced view of global emissions responsibility.
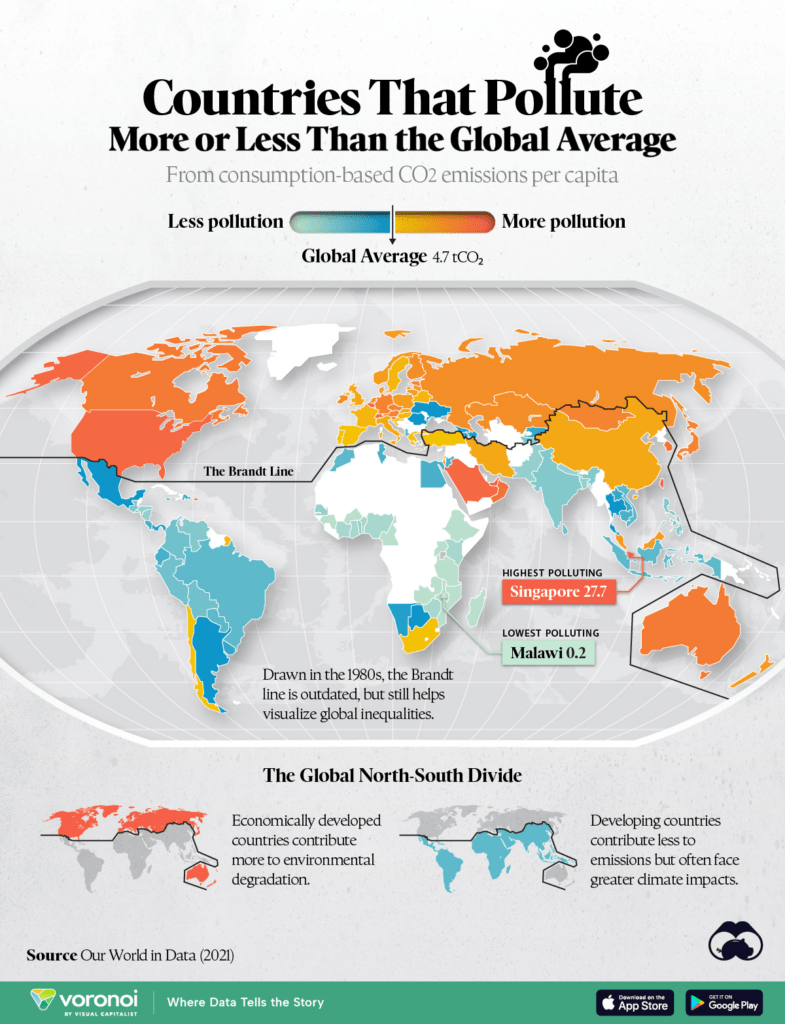
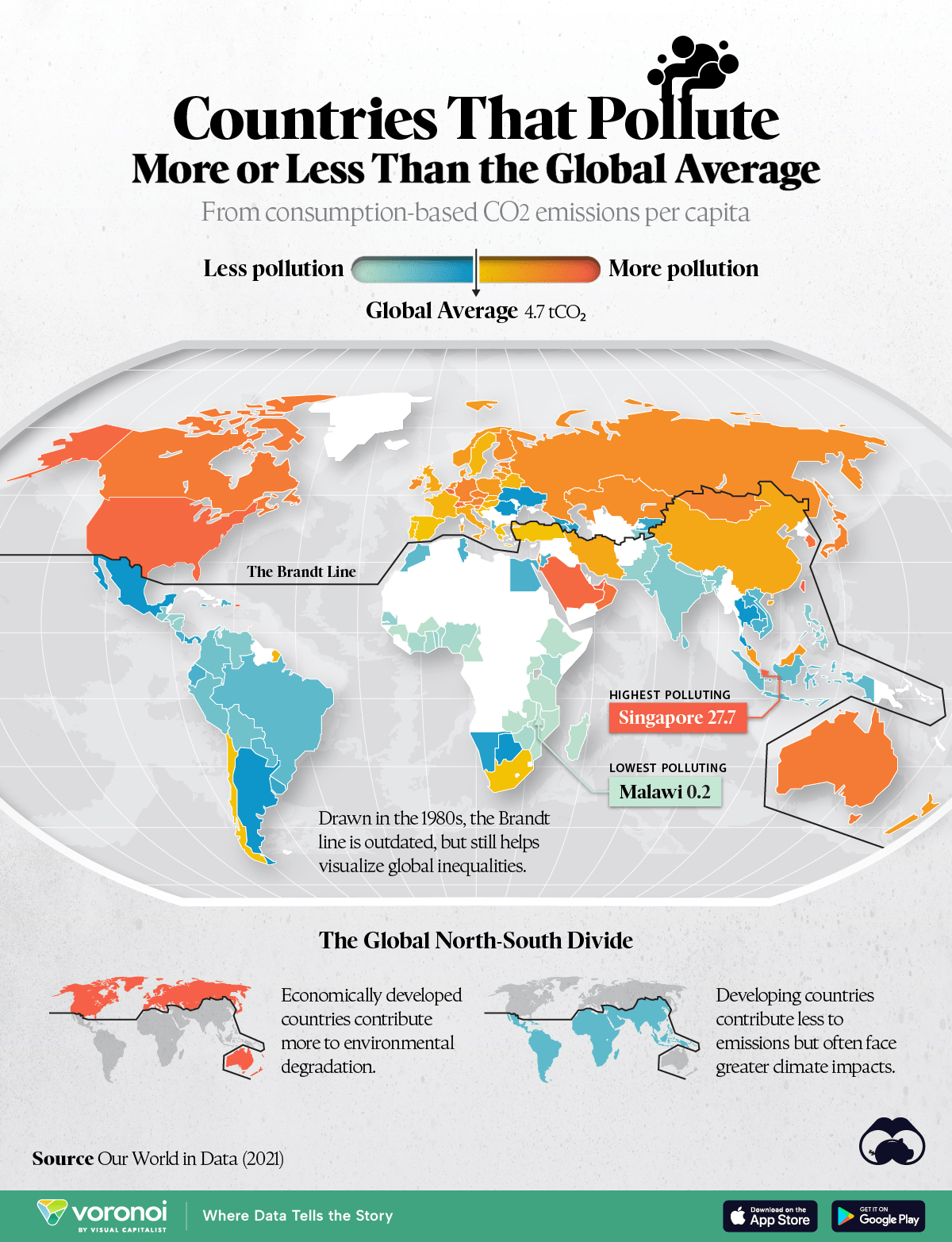
Data from the Global Carbon Budget, as analyzed by Our World in Data, shows that the global average for per capita consumption-based emissions is around 4.7 tons of CO₂. However, this number varies significantly between countries, reflecting the different economic systems, industrial capacities, and consumption habits around the world.
Global North vs. Global South: Disparities in Carbon Footprints
The map of consumption-based carbon emissions per capita highlights a stark divide between the Global North—wealthier, more industrialized nations such as North America, Europe, and parts of Oceania—and the Global South, which includes developing regions such as South America, Africa, and much of Asia. This divide reveals a significant issue in the fight against climate change: those countries contributing the most to emissions are not always the ones bearing the worst consequences.
For instance, in the Global North, countries like the United States (16.5 tons CO₂ per capita), Belgium (17.2 tons), and Australia have much higher per capita emissions compared to nations in the Global South, like India, which has a per capita footprint far below the global average. Despite their lower emissions, countries in the Global South face harsher climate impacts, such as increased droughts, floods, and food insecurity.
Ranked: Countries with the Highest Consumption-Based Carbon Emissions
While much of the Global North has higher emissions, there are several outliers in this narrative. Small, wealthy oil-producing nations in Asia dominate the list of countries with the highest per capita emissions:
- Singapore – 27.7 tCO₂ per capita
- Qatar – 26.7 tCO₂ per capita
- United Arab Emirates – 25.8 tCO₂ per capita
- Kuwait – 24.5 tCO₂ per capita
- Brunei – 21.7 tCO₂ per capita
These countries are not large industrial powerhouses but are instead driven by wealth from fossil fuels, which results in high levels of consumption and emissions.
Solutions by Country to Reduce Sustainability and Waste Impact
Each country faces unique challenges in reducing its carbon footprint, but several strategies can help lower emissions and promote sustainability:
1. Singapore
As a small, densely populated island city-state, Singapore’s high consumption and reliance on imports contribute to its elevated emissions. However, Singapore has been proactive in implementing green policies.
Singapore is investing in green building technologies, public transport electrification, and innovative urban farming to reduce food imports. The country is also expanding solar energy use, with a target of meeting 30% of its energy needs with renewables by 2030.
2. Qatar
Qatar’s economy is heavily dependent on fossil fuel exports, particularly natural gas, which drives its high emissions.
Qatar is diversifying its energy sources by investing in large-scale solar projects, including one of the world’s largest solar plants, Al Kharsaah. It is also focusing on green hydrogen as a future export alternative to natural gas.
3. United Arab Emirates (UAE)
The UAE has a high standard of living and a consumption-heavy economy. To reduce its emissions, the country is pursuing multiple sustainability projects.
The UAE has set ambitious renewable energy targets, including the completion of the Mohammed bin Rashid Al Maktoum Solar Park, the largest solar project in the world. It is also developing waste-to-energy projects and promoting sustainable tourism practices.
4. Kuwait
Kuwait is another oil-rich nation with a high carbon footprint per capita due to its energy consumption patterns.
Kuwait can significantly reduce emissions by implementing energy efficiency measures in its buildings and transportation sectors. The government is also exploring renewable energy options like solar and wind power and improving waste management systems.
5. Brunei
Brunei’s reliance on oil and gas exports has led to high emissions per capita, though the country has vast forested areas that could help offset emissions.
Brunei’s path to sustainability includes expanding forest conservation and promoting eco-friendly practices in the energy sector. Brunei is also exploring carbon capture and storage technologies to mitigate emissions from its oil and gas operations.
Countries in the Global North
United States
The U.S. remains one of the world’s largest emitters, largely due to its dependence on fossil fuels, suburban sprawl, and high levels of consumption.
Solutions for the U.S. include scaling up renewable energy projects, investing in electric vehicles, improving energy efficiency standards in buildings, and transitioning to a circular economy to reduce waste. The Inflation Reduction Act of 2022 is one step in the right direction, offering incentives for clean energy adoption.
Belgium
Belgium’s carbon footprint stems from its industrial sector and energy consumption.
The country is investing in offshore wind farms and hydrogen energy to reduce its reliance on fossil fuels. Additionally, Belgium is improving public transport infrastructure and promoting energy-efficient practices in buildings to curb emissions.
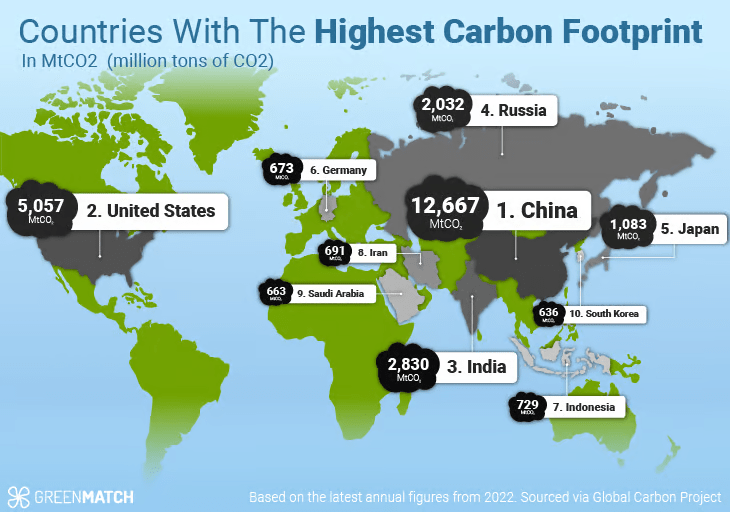
Global South: Addressing Inequities and Promoting Sustainable Development
India
Despite having a lower per capita footprint, India is under pressure to curb its rising emissions as its economy grows.
India is ramping up renewable energy projects, particularly solar and wind. The country aims to install 500 GW of renewable energy by 2030 and reduce its reliance on coal. India is also promoting electric vehicles and improving waste management systems in urban areas.
South Africa
South Africa, one of the few African nations with per capita emissions above the global average, relies heavily on coal for energy.
South Africa is transitioning towards renewable energy, with significant investments in solar and wind power. It has set ambitious targets to phase out coal and improve energy efficiency across industries.
Conclusion: A Collective Effort for a Sustainable Future
Reducing consumption-based carbon emissions is not just the responsibility of individual nations—it is a global effort that requires cooperation, innovation, and equitable solutions. Wealthier nations with higher consumption patterns must lead the way by investing in renewable energy, promoting sustainable lifestyles, and helping developing countries access green technologies. Meanwhile, countries in the Global South need support to develop sustainably without repeating the mistakes of industrialized nations. By working together, we can reduce emissions and promote a more sustainable and just future.
Related Content
- 2024: A Year of Climate Extremes
- Climate Crisis: The Worst Is Yet to Come for Southern France
- Overshooting Climate Targets Could Have Lasting Consequences: A Wake-Up Call
- Global Water Resources Crisis: WMO Report Urges Immediate Action to Combat Climate-Induced Water Shortages
- The Regional Impacts of Climate Change in France: Understanding the Crisis and Finding Solutions
- Unprecedented Floods in the Sahara Desert: A Stark Warning from Climate Change
- Cheapest and Most Expensive Countries for EV Charging in Europe: Understanding the Challenges and Opportunities for Renewable Energy
- Top 10 Richest Countries in 2024 by GDP per Capita: Europe and Asia Lead the Way
- Top Countries by Fossil Fuel Consumption in 2023: A Complex Picture of Growth, Sustainability, and Ecological Impact
- At COP28, over 60 countries commit to reducing cooling-related emissions
- Evolving waste management
- Decreasing carbon intensity and increasing sustainability
- What is circular economy and why does it matter?
- CO₂ and Greenhouse Gas Emissions