Fossil Fuel Consumption Reaches New Highs Amid Rising Environmental Concerns
In 2023, fossil fuel consumption surged to record levels, driven predominantly by increased coal and oil use in China, despite the global expansion of renewable energy sources. This paradoxical trend highlights the ongoing tension between economic growth, energy demand, and environmental sustainability.
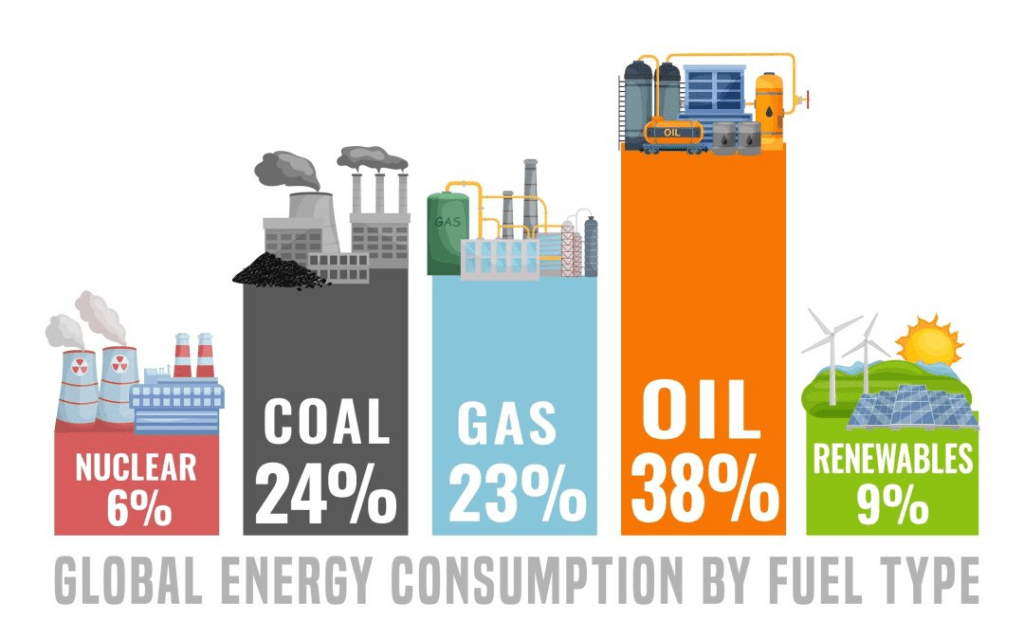
Together, gas, oil, and coal accounted for 81.5% of the global energy mix last year, only slightly down from 82% in 2022. This persistent reliance on fossil fuels underscores the challenges facing the global transition to a cleaner energy future. While renewable energy capacity is growing, it has yet to offset the continued rise in fossil fuel consumption in key economies.
This article examines the top 12 countries by fossil fuel consumption in 2023, drawing data from the Energy Institute’s 2024 Statistical Review of World Energy, released in June 2024.
China and the U.S.: Dominating Global Fossil Fuel Consumption
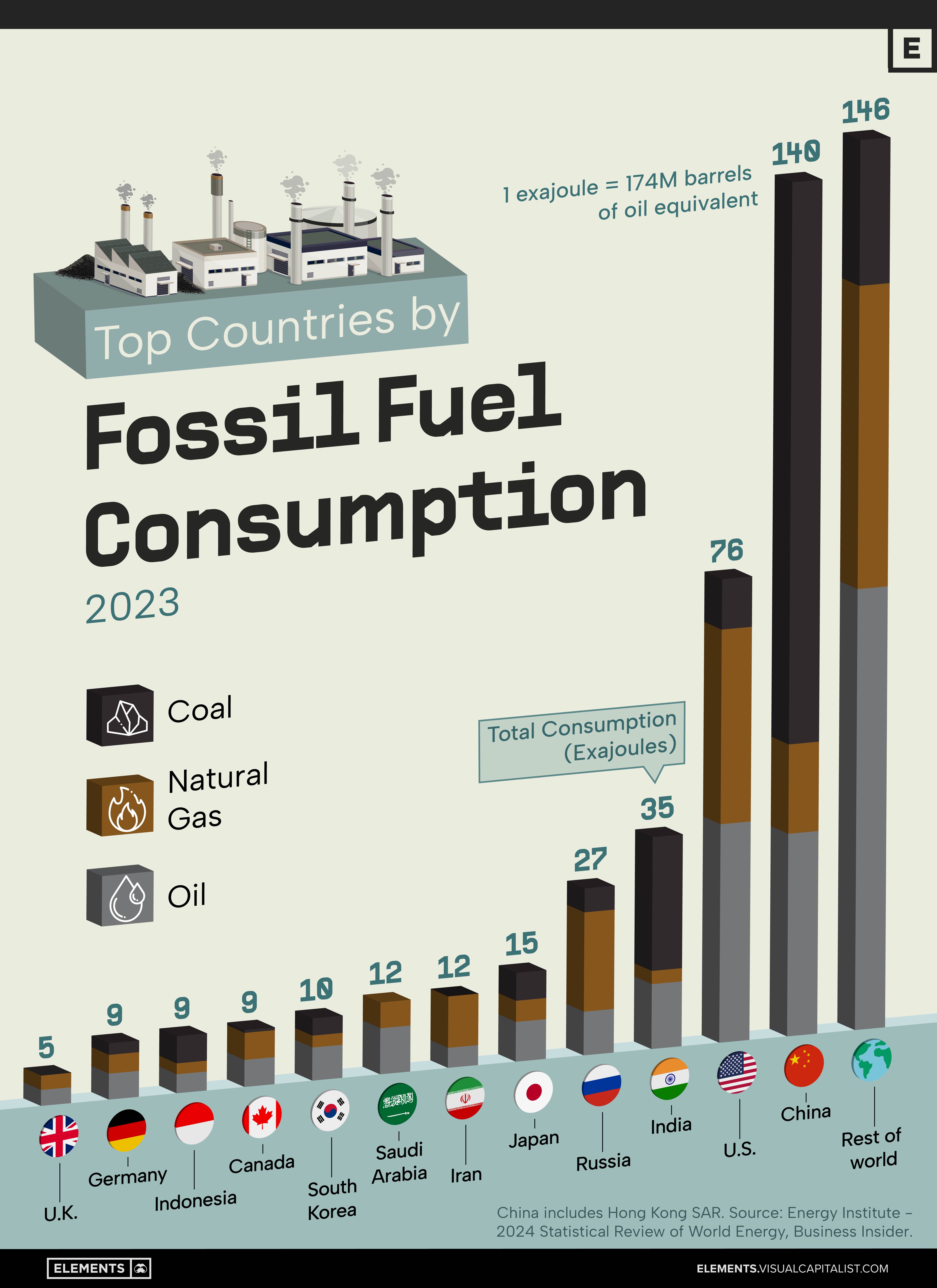
This graphic shows the top 12 countries by fossil fuel consumption in 2023. Data is from the Energy Institute, 2024 Statistical Review of World Energy, released in June 2024.
China and the United States together are responsible for nearly half (47%) of global fossil fuel consumption. China’s fossil fuel consumption reached a staggering 140 exajoules, equivalent to approximately 5.8 billion tonnes of hard coal. The U.S. followed with 76 exajoules, while India was third with 35 exajoules.
| Country | Oil (Exajoules) | Natural Gas | Coal | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 🇨🇳 China | 33 | 15 | 92 | 140 |
| 🇺🇸 U.S. | 36 | 32 | 8 | 76 |
| 🇮🇳 India | 11 | 2 | 22 | 35 |
| 🇷🇺 Russia | 7 | 16 | 4 | 27 |
| 🇯🇵 Japan | 7 | 3 | 5 | 15 |
| 🇮🇷 Iran | 4 | 9 | 0 | 12 |
| 🇸🇦 Saudi Arabia | 7 | 4 | 0 | 12 |
| 🇰🇷 South Korea | 5 | 2 | 3 | 10 |
| 🇨🇦 Canada | 4 | 4 | 0 | 9 |
| 🇮🇩 Indonesia | 3 | 2 | 4 | 9 |
| 🇩🇪 Germany | 4 | 3 | 2 | 9 |
| 🇬🇧 United Kingdom | 3 | 2 | 0 | 5 |
| 🌍 Rest of the World | 72 | 50 | 24 | 146 |
In 2023, China continued to dominate coal consumption, accounting for 56% of global usage, setting a new record for the country. Meanwhile, India’s coal consumption surpassed the combined total of Europe and North America for the first time, highlighting the growing energy needs of emerging economies.
Ecological and Sustainability Considerations
The relentless rise in fossil fuel consumption, especially coal, raises significant ecological concerns. The combustion of fossil fuels is the primary driver of global greenhouse gas emissions, contributing to climate change, air pollution, and a host of environmental problems.
China’s continued reliance on coal poses a particular challenge for global climate goals. Coal is the most carbon-intensive fossil fuel, and its widespread use in China and other developing countries could undermine international efforts to limit global warming to 1.5°C above pre-industrial levels.
Moreover, the environmental impact of increased fossil fuel consumption extends beyond carbon emissions. The extraction, transportation, and use of fossil fuels can lead to habitat destruction, water contamination, and other forms of environmental degradation. For instance, coal mining often results in deforestation and soil erosion, while oil and gas extraction can disrupt fragile ecosystems and lead to oil spills and methane leaks.
The Path Forward: Balancing Growth with Sustainability
Addressing the environmental impact of fossil fuel consumption requires a multifaceted approach. Policymakers must prioritize the expansion of renewable energy, improve energy efficiency, and implement carbon pricing mechanisms to incentivize the reduction of fossil fuel use.
In parallel, there is a critical need for sustainable land use and ecosystem management to mitigate the ecological damage associated with fossil fuel extraction and consumption. Investing in reforestation, wetland restoration, and other nature-based solutions can help absorb carbon emissions and protect biodiversity.
Transitioning to a sustainable energy future is not only about reducing fossil fuel consumption but also about ensuring that economic development does not come at the cost of environmental health. As countries like China and India continue to grow, they will need to balance their energy needs with the imperative to protect the planet for future generations.
Conclusion: The Road Ahead
The record levels of fossil fuel consumption in 2023 underscore the ongoing challenge of achieving global energy sustainability. Despite significant advancements in renewable energy technologies and their growing contribution to the global energy mix, the persistent reliance on fossil fuels reveals a critical gap in our transition efforts. This trend highlights the urgency of not only expanding renewable energy capacity but also implementing robust policies that incentivize energy efficiency and reduce overall consumption.
Sustainability considerations must take center stage as the world grapples with the dual challenge of meeting energy demands while curbing carbon emissions. The continued use of coal, oil, and natural gas exacerbates greenhouse gas emissions, accelerating climate change and its associated impacts, such as extreme weather events, rising sea levels, and loss of biodiversity. Furthermore, the environmental degradation linked to fossil fuel extraction—such as habitat destruction, water pollution, and air quality deterioration—cannot be overlooked.
To move towards a truly sustainable energy future, it is imperative to scale up investments in clean energy infrastructure, enhance grid resilience, and promote the adoption of low-carbon technologies. This includes not only wind, solar, and hydropower but also the development of energy storage solutions and the exploration of next-generation energy sources like green hydrogen. Additionally, global cooperation is essential to support developing nations in their transition to sustainable energy systems, ensuring that economic growth does not come at the expense of the environment.
Only by addressing these challenges head-on and prioritizing sustainability at every level—from local initiatives to international agreements—can we hope to build a more sustainable and resilient energy system for the future. This transition is not merely a technological shift but a fundamental rethinking of how we produce, consume, and value energy, with long-term environmental stewardship as the guiding principle.
Related Content
- Burning a Hole in the Planet: The Devastating Impact of Fossil Fuels on the Environment
- World Environment Day: Illuminating Solutions to Plastic Pollution Worldwide
- Climate Change: Crossing the 1.5°C Threshold Sooner Than Expected
- Lunaz Electrifies the Iconic Aston Martin DB6: A Sustainable Masterpiece
- Ecology, the Olympics, and the Future of Our Planet
- 2024: A Year of Unprecedented Heat
- Global carbon emissions from fossil fuels reached record high in 2023 | Stanford
- Fossil fuel use, emissions hit records in 2023, report says | Reuters
- Renewable Energy Performance Index 2023 – Coincub
- Executive summary – World Energy Outlook 2023 – Analysis – IEA
- World Energy Transitions Outlook 2023 (irena.org)
- Natural resource scarcity, fossil fuel energy consumption, and total greenhouse gas emissions in top emitting countries – ScienceDirect