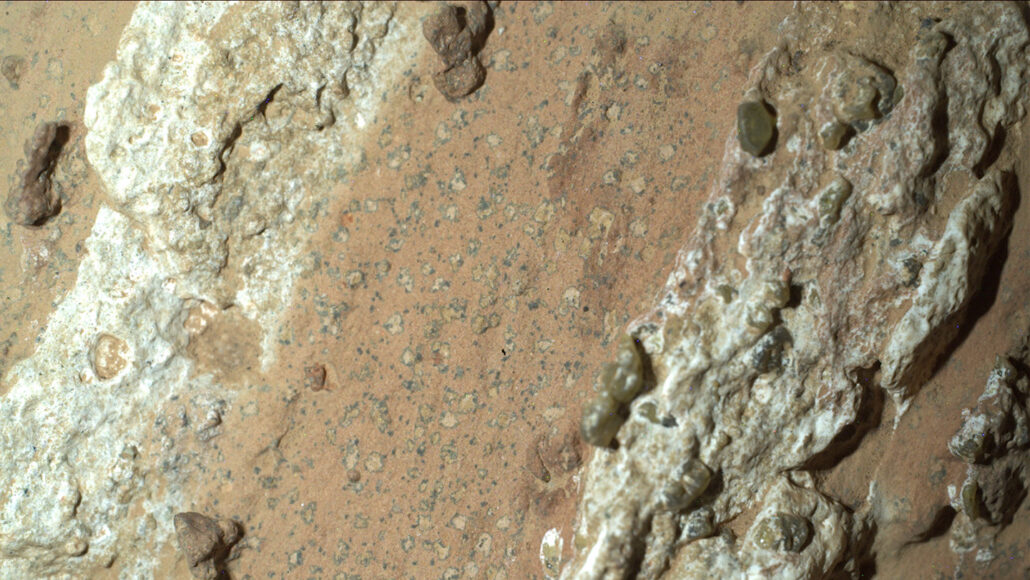
NASA’s Perseverance rover has made a groundbreaking discovery on Mars that could potentially rewrite our understanding of the Red Planet’s history and the possibility of extraterrestrial life.
The Perseverance rover, or “Percy,” as it is fondly called, has uncovered a rock sample on Mars containing organic molecules and mineral formations strikingly similar to structures associated with microbial life on Earth. This discovery, announced by NASA scientists, represents a significant milestone in the quest to determine whether life once existed—or perhaps still exists—beyond our planet.
The Implications of Percy’s Find
The identification of organic molecules—fundamental building blocks of life—and mineral formations akin to those found in Earth’s microbial habitats strongly suggest that Mars may have once harbored conditions conducive to life. This discovery, while not definitive proof of life on Mars, greatly strengthens the hypothesis that the Red Planet may have been more hospitable to life in the distant past.
Mars has long been a subject of fascination due to its similarities to Earth. Scientists believe that billions of years ago, Mars was a warmer, wetter planet, with rivers, lakes, and possibly even oceans. These conditions could have provided a suitable environment for life to emerge. The organic molecules discovered by Perseverance might be remnants of a time when Mars had a more Earth-like environment, offering the tantalizing possibility that life once flourished on our neighboring planet.
The presence of these organic molecules raises important questions about the history of Mars. Were these molecules formed through abiotic processes, or do they point to biological activity? The mineral formations found alongside these molecules could provide clues. On Earth, similar formations are often associated with microbial life, suggesting that ancient Martian microbes might have played a role in shaping the planet’s geology.
The Road Ahead: Returning Samples to Earth
To conclusively determine whether the rock sample truly contains evidence of ancient life, scientists emphasize the importance of returning the sample to Earth. Only then can it be subjected to the rigorous analysis needed to confirm the presence of bio-signatures. The Mars Sample Return mission, a collaborative effort between NASA and the European Space Agency (ESA), aims to retrieve these samples within the next decade.
This mission represents a critical step in our understanding of Mars’ history and its potential to have supported life. By bringing these samples back to Earth, scientists can use advanced laboratory techniques to search for signs of past life, such as fossilized microbial structures, isotopic ratios indicative of biological processes, or complex organic molecules that cannot be easily explained by abiotic chemistry.
The Mars Sample Return mission also has broader implications for planetary protection. By studying Martian samples on Earth, we can better understand the risks of contaminating other planets with Earth life and develop strategies to prevent such contamination during future missions.
Mars and the Search for Extraterrestrial Life
The search for life on Mars is part of a broader scientific effort to understand the origins of life in the universe. If life existed on Mars, it would suggest that life is not unique to Earth and that it could emerge under a wide range of conditions. This would have profound implications for our understanding of biology, chemistry, and the potential for life elsewhere in the universe.
Mars is not the only target in this search. Other bodies in our solar system, such as Europa (a moon of Jupiter), Enceladus (a moon of Saturn), and Titan (another moon of Saturn), are also considered promising candidates for finding extraterrestrial life. These moons have subsurface oceans that could harbor life, and future missions are planned to explore them in greater detail.
However, Mars remains the most accessible and Earth-like of these bodies, making it the primary focus of current efforts. Percy’s discovery is a reminder of the potential that Mars holds for answering one of humanity’s most profound questions: Are we alone in the universe?
Could Mars Help Solve Earth’s Energy and Climate Crises?
While the search for life on Mars captures the imagination, it also intersects with some of the most pressing challenges facing humanity today, particularly in the realms of energy and climate change. As our planet grapples with the twin crises of dwindling energy resources and accelerating climate change, the exploration of Mars offers both a technological testing ground and a source of inspiration for developing sustainable solutions on Earth.
Renewable Energy Innovations
The harsh environment of Mars—characterized by its thin atmosphere, frequent dust storms, and distance from the Sun—presents unique challenges for energy production. These challenges have driven the development of advanced solar power technologies that could be adapted for use on Earth. For example, solar panels designed for Mars missions must be highly efficient, lightweight, and capable of operating in low-light conditions. These innovations could improve the efficiency and reliability of solar power on Earth, making it a more viable alternative to fossil fuels.
Moreover, the need for sustainable energy solutions on Mars has led to advancements in energy storage technologies, such as batteries and fuel cells. These technologies are crucial for storing energy generated by renewable sources and ensuring a stable supply of power during periods when sunlight is unavailable. As we work to transition away from fossil fuels on Earth, the lessons learned from Mars exploration could help accelerate the adoption of clean energy technologies.
Climate Change Insights
Mars exploration also provides valuable insights into the processes that drive climate change. Mars is a prime example of a planet that underwent dramatic climate shifts. Once warm and wet, Mars gradually lost its atmosphere, leading to the cold, arid environment we see today. By studying the history of Mars’ climate, scientists can gain a better understanding of the factors that contribute to climate change on Earth.
One area of particular interest is the role of greenhouse gases in Mars’ climate history. Mars’ atmosphere is primarily composed of carbon dioxide, but it is much thinner than Earth’s atmosphere. Understanding how Mars lost its atmosphere and what impact this had on its climate could provide clues about the long-term effects of greenhouse gas emissions on Earth.
Additionally, the exploration of Mars could inform geoengineering efforts aimed at mitigating climate change. For example, scientists have proposed using mirrors or other technologies to reflect sunlight away from Earth, thereby cooling the planet. Similar concepts could be tested on Mars, where they would not pose a risk to existing ecosystems. The lessons learned from these experiments could help guide the development of geoengineering strategies on Earth.
Mars as a Potential Solution to Earth’s Energy Crisis
As humanity faces the growing challenge of meeting its energy needs while reducing carbon emissions, Mars presents intriguing possibilities for future energy production. While it may seem far-fetched, some scientists and visionaries have proposed harnessing the resources of Mars to help solve Earth’s energy crisis.
One such idea involves the mining of Martian resources, such as water ice, which could be used to produce hydrogen fuel. Hydrogen is a clean and versatile energy carrier that could play a key role in the transition to renewable energy. On Mars, water ice is abundant at the poles and potentially beneath the surface, providing a potential source of hydrogen for fuel cells or other energy systems.
Another possibility is the construction of solar power stations on Mars that could transmit energy back to Earth. This concept, known as space-based solar power, involves capturing solar energy in space and beaming it to Earth using microwave or laser technology. Mars, with its relatively clear skies and proximity to the asteroid belt (a potential source of raw materials), could serve as an ideal location for such power stations.
While these ideas are still in the realm of science fiction, they highlight the potential for Mars exploration to inspire innovative solutions to Earth’s energy challenges. As we continue to explore Mars, we may discover new resources and technologies that could help address the global energy crisis.
The Ethical and Environmental Considerations
As exciting as the possibilities of Mars exploration are, it is crucial to consider the ethical and environmental implications of these endeavors. Space exploration is an energy-intensive activity that contributes to greenhouse gas emissions and other environmental impacts. It is essential to balance the pursuit of scientific knowledge with the need to protect our own planet.
One of the key challenges is ensuring that Mars exploration does not lead to the contamination of the Red Planet with Earth life. Introducing terrestrial microbes to Mars could compromise the search for extraterrestrial life and potentially harm any existing Martian ecosystems. Planetary protection protocols are in place to minimize these risks, but they must be rigorously enforced as we ramp up our exploration efforts.
On Earth, the development of clean energy technologies and sustainable practices is crucial for reducing the environmental impact of space exploration. For example, NASA and other space agencies are increasingly using renewable energy sources and energy-efficient technologies in their missions. Additionally, efforts are being made to reduce the carbon footprint of rocket launches and other activities associated with space exploration.
Ultimately, the goal should be to explore Mars in a way that is sustainable and responsible, ensuring that our pursuit of knowledge does not come at the expense of our own planet or the potential for life on Mars.
The Future of Mars Exploration
Percy’s discovery is a significant milestone in the ongoing exploration of Mars, but it is only the beginning. Future missions to Mars will build on this discovery, searching for more evidence of past or present life and exploring the planet’s geology, climate, and potential resources.
NASA’s Mars Sample Return mission is one of the most anticipated upcoming missions. This mission will retrieve the samples collected by Perseverance and return them to Earth for detailed analysis. The results could provide definitive evidence of ancient life on Mars and offer new insights into the planet’s history.
In addition to sample return missions, future exploration efforts may include the deployment of more advanced rovers, landers, and possibly even human missions to Mars. These missions will explore new regions of the planet, conduct experiments, and test technologies that could one day support human settlement on Mars.
The exploration of Mars is a journey that will continue for decades to come. Each new discovery brings us closer to answering the fundamental questions about the potential for life beyond Earth and the future of humanity in the cosmos.
Mars Exploration and the Human Spirit
The search for life on Mars is more than just a scientific endeavor—it is a testament to the boundless curiosity and determination of the human spirit. For centuries, Mars has been a symbol of mystery and possibility, inspiring countless stories, theories, and dreams. Today, as our technology and scientific understanding advance, we stand on the cusp of turning those dreams into reality.
The discovery made by Perseverance, while not definitive, opens a new chapter in our exploration of Mars. It challenges us to look beyond our own planet and consider our place in the universe. Are we alone, or is life a common thread that weaves through the cosmos? The answer to this question has the potential to redefine our understanding of biology, evolution, and the very nature of life itself.
But the implications of Mars exploration extend beyond the search for extraterrestrial life. As we push the boundaries of what is possible, we also confront some of the most pressing challenges facing our own planet. The innovations and discoveries made on Mars could pave the way for new solutions to Earth’s energy and climate crises. By developing technologies that allow us to thrive in the harsh environment of Mars, we may uncover new ways to live sustainably on Earth.
At the same time, the exploration of Mars reminds us of the importance of stewardship. Just as we must protect Earth’s delicate ecosystems, we have a responsibility to ensure that our exploration of other worlds is conducted ethically and responsibly. The lessons we learn from Mars could help us better understand our own planet and our impact on it, guiding us toward a future where we live in harmony with both our own world and the cosmos beyond.
Mars and the Broader Vision of Space Exploration
Mars is just one destination in humanity’s broader vision of space exploration. As we develop the technologies and capabilities needed to explore Mars, we are also laying the groundwork for future missions to more distant worlds. The skills and knowledge gained from Mars missions will be crucial as we set our sights on more ambitious goals, such as exploring the outer planets and their moons, or even sending humans beyond the solar system.
The potential for Mars to contribute to humanity’s long-term goals in space is significant. Establishing a sustainable presence on Mars could serve as a stepping stone for missions deeper into the solar system. For instance, Mars could act as a refueling station or a hub for missions to the asteroid belt, where resources such as water and metals could be harvested to support further exploration. The development of infrastructure on Mars might also lead to new innovations in space habitats, life support systems, and propulsion technologies.
Moreover, Mars offers a unique opportunity to test the feasibility of human colonization of other planets. While the challenges are immense, the potential rewards are equally great. A successful human settlement on Mars would demonstrate that humanity can survive and thrive beyond Earth, opening the door to a future where human civilization extends across the solar system.

Mars as an Inspiration for Earth
Mars has always been a source of inspiration, and its exploration continues to captivate the imaginations of people around the world. The discoveries made on Mars have the power to unite humanity in a shared quest for knowledge and exploration. In a time when our planet faces significant challenges, the exploration of Mars serves as a reminder of what we can achieve when we work together toward a common goal.
The pursuit of knowledge on Mars can also inspire a new generation of scientists, engineers, and explorers. The challenges of exploring Mars—whether it’s developing new technologies, solving complex problems, or searching for life—encourage innovation and creativity. These efforts not only advance our understanding of Mars but also contribute to technological and scientific progress that benefits all of humanity.
As we continue to explore Mars, it’s essential to remember the importance of public engagement and education. By involving people from all walks of life in the journey to Mars, we can foster a global sense of excitement and curiosity about science, technology, and the future. Whether through citizen science projects, educational programs, or public outreach, the story of Mars can inspire people to pursue their own passions and contribute to the advancement of knowledge.
The Ethical Dilemmas of Colonizing Mars
As discussions about human colonization of Mars gain momentum, they bring with them a host of ethical dilemmas that need to be carefully considered. The idea of establishing a human presence on another planet raises fundamental questions about the rights of the planet itself and the responsibilities of the colonizers.
One major concern is the potential for contamination. Mars may harbor life forms that are as yet undiscovered, and the introduction of Earth-based organisms could threaten these indigenous species, if they exist. Even in the absence of life, introducing Earth’s biosphere to Mars could irreversibly alter its environment, potentially contaminating the very evidence we seek to find. As we plan for future missions, it is vital to weigh the risks of contamination against the potential benefits of exploration.
The question of planetary ownership and governance also arises. If humans were to establish colonies on Mars, who would govern these new societies? What legal and ethical frameworks would guide their development? The notion of “space law” is still in its infancy, and the colonization of Mars could prompt the need for new international agreements that address issues like resource allocation, environmental protection, and the rights of future Martian inhabitants.
Mars and the Future of Humanity
The exploration and potential colonization of Mars present both incredible opportunities and profound challenges. While the Red Planet may one day serve as a new frontier for human civilization, it also forces us to confront fundamental questions about our values, our responsibilities, and our place in the universe.
As we look to the future, it is essential to approach Mars exploration with a sense of humility and caution. The discoveries we make on Mars could reshape our understanding of life, the cosmos, and our own planet. But they also carry the risk of unintended consequences, both for Mars and for Earth.
In the end, the story of Mars is not just about the search for extraterrestrial life or the potential for human colonization. It is also a story about our own humanity—our curiosity, our ambition, and our ability to imagine a future that is bigger than ourselves. As we continue to explore Mars, we must strive to do so in a way that honors both the potential of the Red Planet and the legacy we hope to leave behind.
The Next Frontier
NASA’s Perseverance rover has opened a new chapter in the exploration of Mars, one that holds the promise of groundbreaking discoveries and the potential for profound implications. As we continue to study the Red Planet, we stand on the brink of answering some of the most enduring questions in science: Are we alone in the universe? What does the future hold for human exploration? And how can the lessons we learn from Mars help us solve the challenges facing our own planet?
Mars is more than just a destination; it is a symbol of what we can achieve when we push the boundaries of knowledge and imagination. The discoveries we make on Mars will not only deepen our understanding of the universe but also inspire new ways of thinking about our place within it. As we embark on this journey, we do so with the hope that the exploration of Mars will lead to a better future for all of humanity.
Related Content
- ‘Percy’, NASA’s rover, finds its first hint of ancient life on Mars
- Terraforming Mars: A Potential Breakthrough or a Cautionary Tale?
- Mars colonists will be able to breathe oxygen massively thanks to artificial intelligence
- Tesla’s Giga Train: Revolutionizing Public Transit with Ecological Impact
- The Intersection of Wealth, Sustainability, and Climate Change in 2024
- Save The Planet Conservation Sticker – Eco-Friendly Car Window Decal – Vinyl Material – Scratch Resistant – Adhesive Backing – Suitable for Cars, Laptops, and More
- Getting Teased for Doing It for the Planet”: The Struggles of Going Vegetarian in a BBQ-Centric World
- Ecology, the Olympics, and the Future of Our Planet
- Support Your Local Planet Tote Bag: Eco-Friendly Shopping and Picnic Companion
- Sustainable Living: How You Can Help Preserve Our Planet
- Preserving Our Planet: A Comprehensive Guide to Environmental Conservation
- Searching for Life in NASA’s Perseverance Mars Samples
- Mars 2020 mission to search for past microbial life
- Did Perseverance find life on Mars? – Ad Astra
- Percy starts the search for life on Mars

