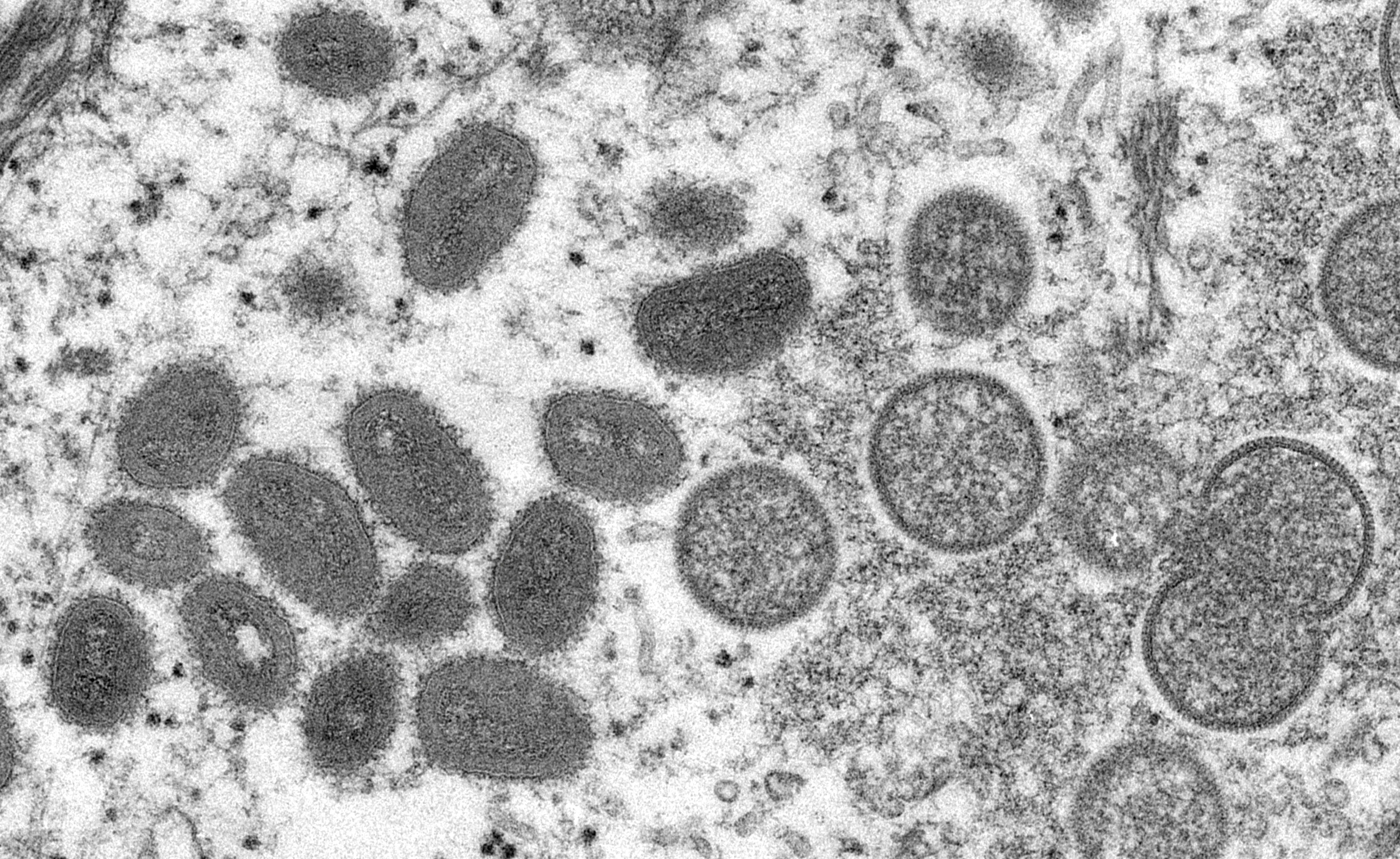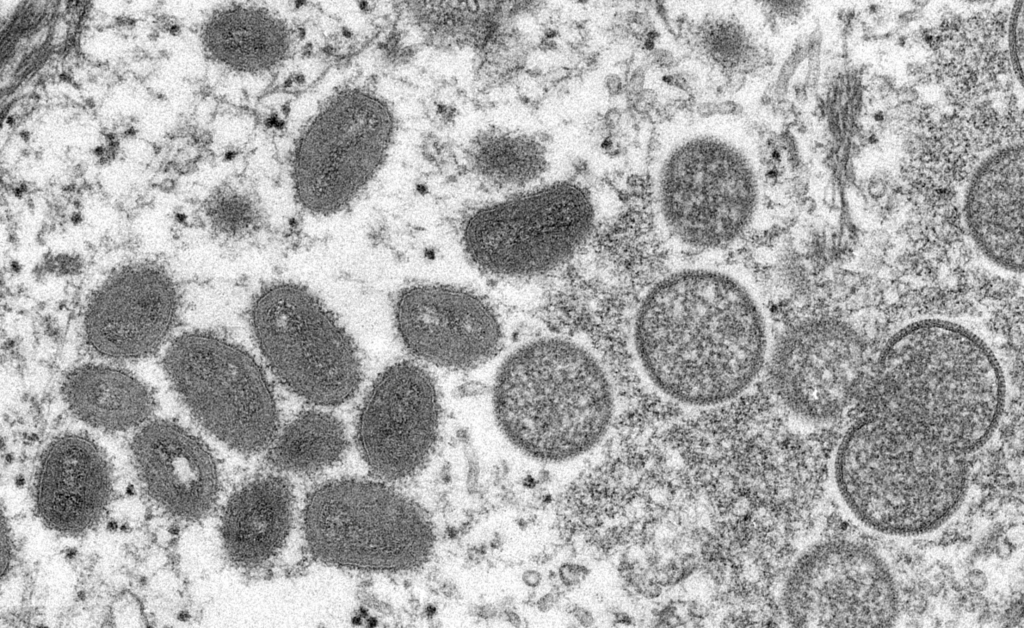
Monkeypox, a rare viral disease with origins in animals, has recently gained attention for its potential to jump from wildlife to humans, echoing concerns reminiscent of past pandemics. Caused by the monkeypox virus, a relative of the smallpox virus, this infectious disease presents a unique set of challenges for public health authorities and scientists. Understanding the nature of monkeypox, its transmission, and potential implications for human health is crucial as we navigate the complex landscape of emerging infectious diseases.
Origins and Transmission
Monkeypox finds its roots in the animal kingdom, with various mammals serving as potential hosts. The virus is believed to be transmitted to humans through contact with infected animals, primarily rodents and monkeys. In some instances, human-to-human transmission has been observed, raising concerns about the disease’s potential for sustained outbreaks. Though cases are relatively rare, the ability of the virus to cross species barriers underscores the importance of vigilance in monitoring and managing zoonotic diseases.
Clinical Presentation and Similarities to Smallpox
Monkeypox shares clinical similarities with smallpox, a disease eradicated through successful vaccination campaigns in the late 20th century. The symptoms include fever, headache, muscle aches, and a characteristic rash, making diagnosis challenging without laboratory testing. While smallpox has been eradicated, the similarities between the two viruses highlight the importance of robust surveillance systems to detect and respond to potential outbreaks promptly.
Global Concerns and Preparedness
The global interconnectedness of today’s world raises concerns about the potential for monkeypox to spread across borders. International cooperation in surveillance, research, and response strategies is crucial to prevent and mitigate the impact of emerging infectious diseases. The World Health Organization (WHO) and other health agencies play a pivotal role in coordinating efforts to monitor and manage diseases like monkeypox, emphasizing the need for a collaborative and preemptive approach to global health security.
Research and Vaccine Development
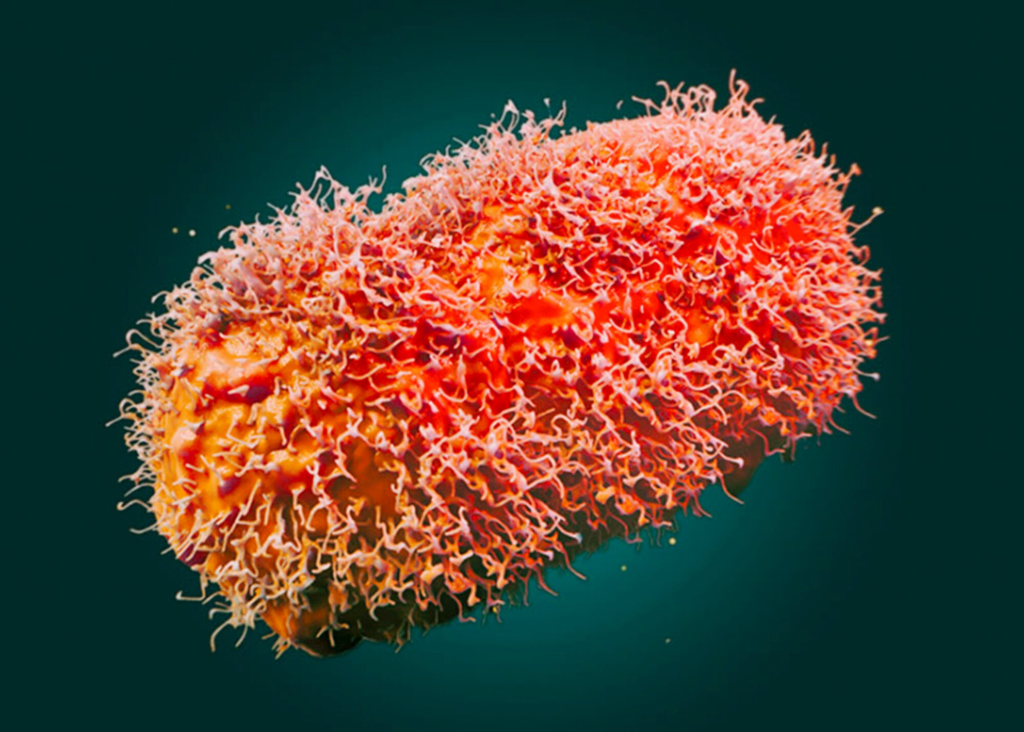
Given the close relationship between the monkeypox and smallpox viruses, research efforts are underway to understand the dynamics of monkeypox transmission and develop effective vaccines. The development of a specific monkeypox vaccine could prove instrumental in preventing outbreaks and controlling the spread of the virus. International collaboration among researchers, pharmaceutical companies, and public health organizations is crucial for expediting the development and distribution of vaccines and treatments.
As the scientific community delves into the intricacies of monkeypox, research becomes a cornerstone in understanding the virus’s behavior, transmission patterns, and potential mutations. Robust research efforts can contribute to the development of targeted diagnostic tools and therapeutics. By investing in research, we can not only enhance our understanding of monkeypox but also bolster our preparedness against future zoonotic threats.
Public Awareness and Prevention
Public awareness plays a pivotal role in preventing the spread of monkeypox. Educating communities, especially those in regions where the virus is prevalent, about the risks associated with handling animals and the importance of seeking medical attention in case of symptoms, is essential. Additionally, promoting hygienic practices, such as handwashing and the use of protective equipment when handling potentially infected animals, can reduce the risk of transmission.
Surveillance and Early Detection
A key component of managing infectious diseases is a vigilant surveillance system capable of detecting outbreaks early on. Establishing and strengthening global surveillance networks, particularly in regions where the virus is known to circulate, is critical. Timely identification of potential cases can facilitate rapid response measures, helping to contain the spread and minimize the impact on public health.
International Cooperation and Information Sharing
The interconnectedness of our world necessitates a collaborative effort among nations, health organizations, and research institutions. International cooperation is indispensable for sharing information, resources, and expertise. This collaborative approach can expedite the development of diagnostic tools and vaccines, ensuring that the global community is well-equipped to respond swiftly to any emerging infectious threat, including monkeypox.
Capacity Building and Infrastructure Development
The imperative to invest in healthcare infrastructure in vulnerable regions extends beyond a single facet of disease prevention—it encompasses a comprehensive strategy for building resilience and fortifying global health security. Strengthening local healthcare systems is a multifaceted approach that not only addresses immediate healthcare needs but also lays the groundwork for long-term sustainability and responsiveness.
Strengthening Primary Healthcare Services
Focusing on primary healthcare services forms the backbone of an effective healthcare infrastructure. By investing in accessible and well-equipped primary care facilities, vulnerable regions can improve their capacity to provide timely and accurate diagnoses, offer essential preventive measures, and facilitate early interventions. Strengthening these foundational healthcare services fosters a resilient healthcare system capable of withstanding the challenges posed by infectious diseases.
- Training and Capacity Development:
The training and professional development of healthcare professionals are pivotal components of building a robust healthcare infrastructure. Investing in continuous education and training programs for doctors, nurses, and other healthcare workers equips them with the knowledge and skills necessary to address emerging threats. This, in turn, ensures a well-prepared workforce capable of swift and effective responses to infectious disease outbreaks. - Establishing Surveillance and Reporting Systems:
Building resilience against infectious diseases requires the implementation of robust surveillance and reporting systems. Investing in technologies for disease monitoring, data collection, and analysis enhances a country’s ability to detect potential outbreaks at an early stage. Timely and accurate information is essential for mounting effective responses, isolating affected individuals, and implementing preventive measures to contain the spread of the disease. - Ensuring Access to Essential Resources:
Adequate and consistent access to essential resources, including medical supplies, vaccines, and diagnostic tools, is critical for healthcare systems to function optimally. Investment in supply chain management and the establishment of stockpiles can mitigate shortages during emergencies, ensuring that healthcare providers have the necessary resources to respond promptly and efficiently to infectious diseases. - Community Engagement and Empowerment:
A resilient healthcare infrastructure goes hand in hand with community engagement and empowerment. Investing in public health education programs, community outreach initiatives, and the promotion of health literacy empowers individuals to actively participate in disease prevention. By fostering a sense of collective responsibility, communities become partners in the broader effort to build resilience against infectious diseases. - Global Collaborations for Sustainable Impact:
Capacity building on a global scale involves collaborative efforts between nations, international organizations, and non-governmental entities. Sharing knowledge, expertise, and resources across borders creates a network of support that strengthens the collective ability to respond to infectious diseases. By fostering partnerships, the global community can leverage collective strengths to address health disparities and enhance global health security.
Investing in healthcare infrastructure in vulnerable regions is an investment in the collective security of the global community. It is a commitment to building resilient healthcare systems that can effectively detect, respond to, and mitigate the impact of infectious diseases. Through strategic and sustained efforts, nations can foster a world where health disparities are reduced, and all communities have the capacity to confront and overcome the challenges posed by emerging health threats.
Public Health Education and Communication
Empowering communities with knowledge about the risks associated with monkeypox and similar diseases is crucial for prevention. Public health campaigns can play a pivotal role in disseminating information about hygiene practices, the dangers of handling potentially infected animals, and the importance of seeking medical attention at the onset of symptoms. Informed and engaged communities are better equipped to contribute to disease prevention efforts.
In Short
In the wake of the potential threat posed by the monkeypox virus, it becomes increasingly evident that a proactive and unified approach is paramount in addressing the complexities of emerging infectious diseases. The lessons learned from previous pandemics, such as the ongoing battle against COVID-19, underscore the need for a global commitment to research, surveillance, and preventive measures to safeguard public health. The threat posed by monkeypox underscores the ongoing challenges of navigating an interconnected world fraught with emerging infectious diseases. By prioritizing research, bolstering surveillance systems, fostering international collaboration, investing in healthcare infrastructure, and educating the public, the global community can fortify its defenses against not only monkeypox but also other potential threats on the horizon. The collective response to such challenges will determine our ability to safeguard public health and build a resilient global health system for the future.
Related Content
- Sufjan Stevens ‘learning to walk again’ after autoimmune disease diagnosis
- Former mayor of London Ken Livingstone diagnosed with Alzheimer’s disease
- Libya floods: appeals for body bags amid fears of disease ‘epidemic’
- Cureus | Unraveling Monkeypox: An Emerging Threat in Global Health
- Concern as experts link monkeypox virus to bush-meat consumption – New Telegraph