Taiwan has made significant strides in implementing machine learning (ML) in its healthcare system, achieving remarkable results in reducing mortality rates and antibiotic costs. Within a year of implementing ML-powered tools, Taiwanese hospitals have witnessed a 25% drop in mortality rates and a 30% decrease in antibiotic expenses.
AI and Machine Learning: A Transformative Force in Healthcare
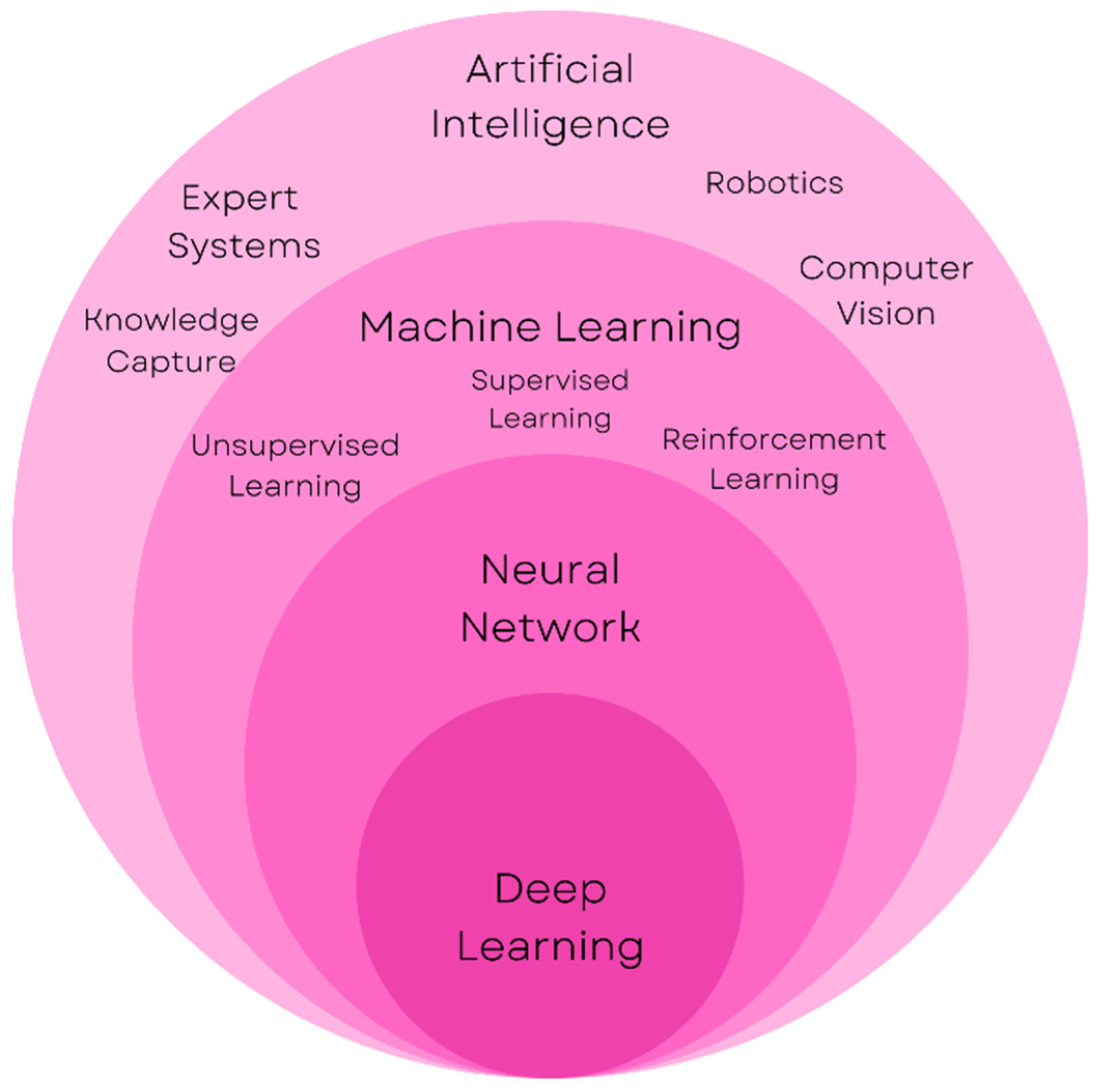
Machine learning, a subset of artificial intelligence (AI), has revolutionized various industries, including healthcare. ML algorithms can analyze vast amounts of data, identify patterns, and make predictions, enabling healthcare providers to make informed decisions, improve patient outcomes, and optimize resource allocation.
Taiwan’s Pioneering Role in AI-Powered Healthcare
Taiwan’s China Medical University Hospital (CMUH) has emerged as a pioneer in adopting ML in healthcare. In collaboration with Microsoft and its Azure data management subsidiary, CMUH has developed and deployed ML-powered tools that are transforming patient care.
Impressive Results: A Model for Other Countries
The results of CMUH’s ML initiatives have been impressive. The hospital has reported a 25% reduction in mortality rates among patients with sepsis, a severe infection that can lead to organ failure and death. Additionally, CMUH has seen a 30% decrease in antibiotic usage, contributing to reduced antibiotic resistance and its associated healthcare costs.
France’s Approach to AI in Healthcare: A Different Path
In contrast to Taiwan’s rapid adoption of ML in healthcare, France has taken a more cautious approach. The French healthcare system is still in the process of digitizing its operations and integrating different healthcare software systems. While AI is not yet widely used in French hospitals, the country is recognizing its potential to improve patient care and cost-effectiveness.
Lessons from Taiwan: A Call to Action
Taiwan’s groundbreaking achievements in integrating Machine Learning (ML) into its healthcare system serve as a blueprint for nations like France seeking to enhance their medical services through technological innovation. To replicate Taiwan’s success, it is essential for countries to invest significantly in ML research. The advancements witnessed in Taiwan’s China Medical University Hospital underscore the transformative potential of ML in healthcare, ranging from precise diagnostics to more effective treatment strategies.
In order to fully embrace ML’s potential, countries must establish robust regulatory frameworks that facilitate the responsible adoption of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in healthcare. Striking the right balance between encouraging innovation and ensuring patient safety is crucial. Taiwan’s experience emphasizes the importance of aligning regulations with technological advancements, allowing healthcare systems to leverage ML capabilities without compromising on ethical and safety standards.
Collaboration is another key takeaway from Taiwan’s journey. Successful integration of ML into healthcare requires strong partnerships among various stakeholders, including healthcare providers, technology companies, and policymakers. Taiwan’s collaboration with Microsoft’s Azure in developing an AI-driven medical assistant exemplifies the impact of such partnerships in achieving groundbreaking results. France, too, should encourage collaboration to create an ecosystem that fosters the seamless integration of ML into its healthcare infrastructure.
As nations grapple with rising healthcare costs, ML presents an opportunity to optimize resource allocation and reduce unnecessary expenditures. By learning from Taiwan’s success, France can develop strategies to curtail costs, enhance patient care, and improve overall healthcare efficiency. It is essential for policymakers to prioritize the development of comprehensive AI-driven solutions, ensuring that healthcare professionals have access to advanced tools that facilitate data-driven decision-making.
In conclusion, Taiwan’s success story with ML in healthcare offers a roadmap for other nations, urging them to invest in research, establish supportive regulatory frameworks, and foster collaboration. Embracing ML in healthcare is not just a technological leap; it’s a commitment to delivering more effective, accessible, and cost-efficient healthcare services for the benefit of populations around the world.
Latest News and Updates
- CMUH Continues to Expand ML Applications: CMUH is actively exploring new applications of ML in healthcare, including using ML to predict patient risk factors and personalize treatment plans.
- Taiwanese Government Supports AI Adoption: The Taiwanese government is committed to promoting AI adoption in healthcare and has launched initiatives to support AI research and development.
- Global Recognition of Taiwan’s Achievements: Taiwan’s success in using ML in healthcare has been recognized internationally, with several healthcare organizations and governments seeking to learn from Taiwan’s experience.
In Short
In the span of just one year, Taiwan’s trials with AI, particularly in the prestigious China Medical University Hospital, have achieved groundbreaking results. The integration of Machine Learning, coupled with Artificial Intelligence, has not only reduced mortality rates by a significant 25% but has also led to a remarkable 30% reduction in antibiotic costs. This achievement underscores the immense potential of AI to revolutionize healthcare, offering more precise diagnoses and treatment strategies.
One key aspect of Taiwan’s success lies in its strategic collaboration with Microsoft’s Azure, emphasizing the importance of partnerships in implementing AI solutions effectively. The technology is not merely confined to a desktop application; it serves as an artificial medical assistant, aiding healthcare professionals in their decision-making processes. This partnership has facilitated the creation of a sophisticated AI tool capable of processing vast amounts of medical data, providing valuable insights that contribute to more informed medical decisions.
Contrastingly, in France, the adoption of AI in healthcare faces distinctive challenges. While the nation is in the process of digitizing its healthcare systems, various proprietary software and limited data exchange capabilities hinder seamless integration. Unlike Taiwan, where the emphasis is on creating a comprehensive AI-driven medical assistant, France’s current trajectory involves digitalizing databases capable of exchanging information. The absence of standardized interfaces and the prevalence of different proprietary systems pose challenges for the widespread adoption of AI technologies.
Taiwan’s success in reducing the cost of antibiotics is particularly noteworthy. In the face of rising healthcare expenditures globally, such efficiencies become imperative. France, grappling with high healthcare costs, could benefit significantly from AI’s ability to curtail unnecessary spending, provided there is a commitment to overcoming existing regulatory and structural barriers.
As countries worldwide strive to deliver quality healthcare in a cost-effective manner, lessons from Taiwan’s AI-driven healthcare initiatives serve as a beacon of hope. The potential of AI to enhance medical outcomes, streamline processes, and reduce expenses is a vision that can be realized globally with thoughtful integration and collaborative efforts. The success of Taiwan’s healthcare transformation underscores the urgency for nations, including France, to explore and embrace AI solutions to optimize their healthcare systems for the benefit of patients and providers alike.
Related Content
- AI and machine learning TorchServe servers vulnerable to malware attacks
- AI Machine Learning trainings
- Whisper V3: The Revolution in Audio-to-Text Transcription
- Navigating the Green Frontier: Quality Control Engineers and the Sustainable Future
- AI-Enabled Mobile Health App for Empowering LMIC s
- Inventing tomorrow’s technology with hyperdimensional computing
- Inside Taiwan’s ‘AI hospital of the future’
- Azure Cloud Computing