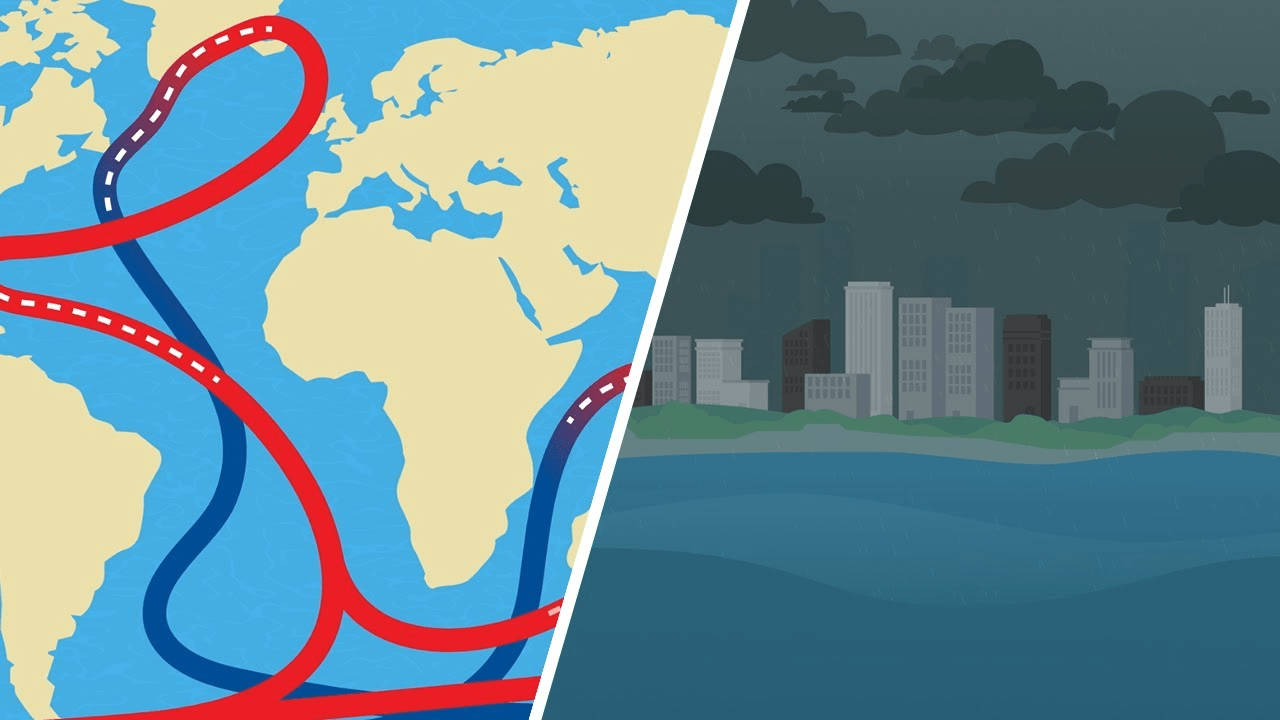
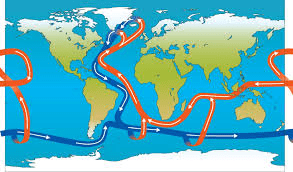
Climate scientists have sounded alarms regarding the potential collapse of the Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation (AMOC), a vital ocean current that significantly influences global climate patterns. The AMOC is a crucial component of the Earth’s climate system, responsible for transporting warm water from the tropics to the North Atlantic, where it cools and sinks before returning south. A disruption or collapse of this system could lead to dire consequences, especially for the Nordic countries and other regions worldwide. This article will explore the implications of a potential AMOC collapse and outline solutions to mitigate the risk.
Understanding the AMOC’s Importance
The AMOC plays a pivotal role in regulating temperatures and weather patterns across the Northern Hemisphere. Its influence extends beyond the Atlantic Ocean, affecting climates as far away as North America, Europe, and even Asia. The current is a critical mechanism in maintaining the balance of heat and salinity in the oceans, and it is intricately linked to the global climate system.
A collapse of the Atlantic Meridional Overturning Current (AMOC) could dramatically alter the climate of the Northern Hemisphere, with Europe and North America likely to face significantly colder winters. Studies suggest that winter temperatures in regions like the UK could drop by several degrees, resulting in harsher and more extreme weather. This shift would occur due to a reduced flow of warm water into the North Atlantic, causing regional climates to cool as warm ocean currents diminish.
The AMOC also plays a critical role in controlling sea levels along the Atlantic coast. Its collapse could raise sea levels, especially along the eastern United States and parts of Europe. This rise is linked to a process called “water piling,” where the warmer waters typically circulated by the AMOC remain stagnant, resulting in elevated local sea levels. For coastal communities, this could mean increased flooding, coastal erosion, and risks to infrastructure and ecosystems.
In addition to cooling and rising sea levels, an AMOC collapse could disrupt established rainfall patterns, leading to extreme events like droughts and floods. The AMOC’s distribution of freshwater in the North Atlantic influences precipitation in regions worldwide. Disruptions could bring less rainfall to areas like the Sahel in Africa, while intensifying precipitation in places such as the Caribbean and southeastern United States. These shifts would exacerbate the impacts of climate change, adding to the urgency of addressing and mitigating AMOC instability.
In light of these alarming predictions, scientists are urging Nordic ministers and global leaders to take immediate action to prevent the collapse of the AMOC. The consequences of inaction could be catastrophic and irreversible.
Root Causes: Greenhouse Gas Emissions
The primary driver of climate change is the increase in greenhouse gas emissions, largely from human activities such as burning fossil fuels, deforestation, and industrial processes. These emissions trap heat in the atmosphere, leading to global warming, which affects ocean currents, including the AMOC.
Solutions to Prevent the Collapse of the AMOC
To mitigate the risk of AMOC collapse, immediate and coordinated action is essential. Transitioning to renewable energy sources is essential for reducing greenhouse gas emissions. By investing in solar, wind, hydroelectric, and geothermal systems, countries can move away from fossil fuels and toward cleaner, more sustainable energy. Improving energy efficiency across buildings, transportation, and industrial sectors will further decrease emissions. To drive this transition, governments should support the adoption of clean technologies through incentives and enforce stringent emissions regulations that encourage sustainable practices and innovation.
As the impacts of climate change continue to escalate, investing in climate adaptation measures becomes increasingly vital. Governments and communities must develop protective infrastructure, like sea walls and natural barriers such as wetlands and mangroves, to guard against rising sea levels and extreme weather. Additionally, research and development in drought-resistant crops will be crucial in addressing food insecurity caused by changing precipitation patterns, helping to build resilience in the agricultural sector.
Addressing climate change demands global collaboration, as it is a challenge that transcends national borders. Countries must join forces to create and implement robust climate policies that target both emissions reductions and adaptive strategies. This global cooperation can manifest through treaties, shared research efforts, and financial aid directed at developing nations that face disproportionate effects of climate change. By working together, countries can better address the root causes and mitigate the far-reaching impacts of climate change.
The Role of Technology and Innovation
In addition to policy changes, technological innovation will play a crucial role in combating climate change and its impacts on the AMOC.
Technologies for Carbon Capture and Storage (CCS) offer a valuable approach to mitigating climate change by capturing carbon dioxide emissions from sources like power plants and industrial facilities. Through CCS, CO₂ can be prevented from reaching the atmosphere, helping to reduce the overall carbon footprint of industrial processes. When used alongside a transition to renewable energy sources, CCS can be an effective tool for managing emissions during the shift to a low-carbon economy.
Implementing sustainable agricultural practices is another powerful way to support climate mitigation while enhancing ecosystem health. Techniques like agroforestry, crop rotation, and organic farming not only reduce emissions but also improve soil health and promote biodiversity. By promoting carbon sequestration within the soil, these practices contribute to lowering greenhouse gas concentrations, reinforcing agriculture’s role in addressing climate change.
Developing climate-resilient infrastructure is essential for adapting to the inevitable impacts of climate change. This includes retrofitting existing buildings to better withstand extreme weather and ensuring that new infrastructure projects incorporate climate projections. Planning for resilience now will help safeguard communities and reduce the long-term costs associated with climate-related damages, creating a foundation for sustainable growth in the face of changing environmental conditions.
A Call to Action
The warning from climate scientists about the potential collapse of the Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation is a wake-up call for governments and communities worldwide. The consequences of such a collapse are severe, with implications for weather patterns, sea levels, and global precipitation. However, by taking proactive steps to address the root causes of climate change, we can work toward preventing this dire outcome.
Reducing greenhouse gas emissions, investing in climate adaptation measures, and fostering international cooperation are critical components of a comprehensive strategy to protect the AMOC and our planet. The time for action is now—every moment we delay increases the risk of catastrophic climate impacts that could last for generations.
Related Content
- Warning of a forthcoming collapse of the AMOC
- The Global Climate Crisis: Bridging the Emissions Gap
- Understanding the Climate Crisis
- Southeast Asian Nations Join BRICS: Implications for Climate Action and Sustainability
- 2024: A Year of Climate Extremes
- Climate Crisis: The Worst Is Yet to Come for Southern France
- Overshooting Climate Targets Could Have Lasting Consequences: A Wake-Up Call
- Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation» (AMOC)
- ‘We don’t know where the tipping point is’: climate expert
- Key Atlantic current could collapse soon