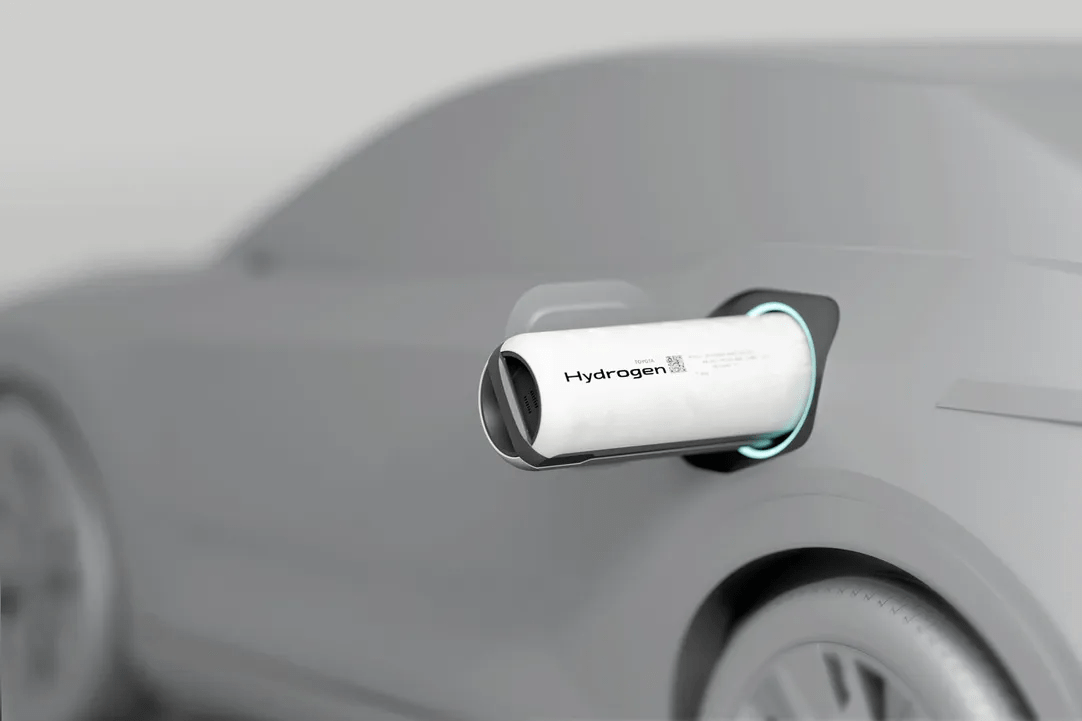
Toyota has been at the forefront of clean automotive innovation, pioneering technologies like hybrid vehicles and hydrogen fuel cell vehicles (HFCVs). However, its recent advocacy for hydrogen as the future of transportation has sparked debate. While HFCVs offer zero tailpipe emissions, their overall environmental impact depends on production methods, efficiency, and infrastructure. This article explores hydrogen’s challenges, contrasts it with battery electric vehicles (BEVs), and proposes solutions for sustainable transportation.