In a groundbreaking development that could reshape the future of renewable energy, Chinese researchers have achieved a world-record efficiency of 29.36% with their newly developed four-terminal (4T) perovskite-CIGS tandem solar cells. This remarkable breakthrough not only sets a new benchmark in solar energy conversion but also highlights the transformative potential of perovskite, a material once deemed “impossible” for practical use.
The Rise of Perovskite: From Impossible to Indispensable
Perovskite, a material discovered in the 19th century, has long fascinated scientists due to its unique crystal structure. However, early attempts to use perovskite in solar cells were met with significant challenges. The material exhibited poor efficiency and even worse stability, degrading rapidly under environmental conditions such as heat and moisture. For decades, perovskite was considered unsuitable for commercial applications, earning it the label of an “impossible material.”
Despite these setbacks, researchers persisted in their efforts to unlock perovskite’s potential. Advances in material engineering have now transformed perovskite into one of the most promising materials for solar energy. Today, perovskite-silicon tandem cells are achieving efficiencies of up to 40%, and standalone perovskite cells continue to break new ground. The recent development of the 4T perovskite-CIGS tandem solar cell is a testament to how far this material has come, proving that perovskite is no longer just an ideal—it is a reality shaping the future of renewable energy.
How the Perovskite-CIGS Tandem Solar Cell Works
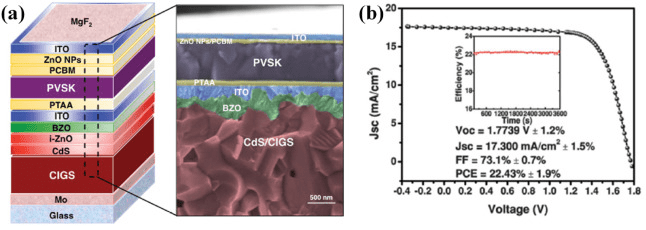
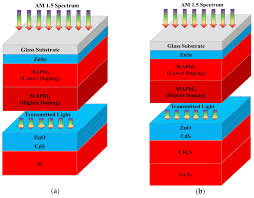
The breakthrough was achieved by scientists at Northwest Normal University, who combined a perovskite-based top cell with a copper-indium-gallium-selenide (CIGS) bottom cell. This tandem structure allows the solar cell to capture a broader spectrum of sunlight, significantly improving its overall efficiency.
The perovskite layer is semi-translucent, enabling some light to pass through to the CIGS bottom layer. This multi-layered approach ensures that high-energy photons are absorbed by the perovskite top cell, while low-energy photons are captured by the CIGS bottom cell. By optimizing the use of different wavelengths of sunlight, the tandem cell achieves unprecedented energy conversion rates.
To enhance the quality of the perovskite layer, researchers employed a solvent-annealing method using dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO). The material was then heated twice—first at 100°C and later at 80°C—to promote crystal growth. The result was a high-purity perovskite film with improved crystallinity and larger grain sizes, free from lead iodide contamination. This innovation enabled the team to achieve a semi-transparent perovskite top cell efficiency of 21.26%, with a bifaciality factor of 92.2%. When combined with the CIGS bottom cell, the tandem structure reached an overall efficiency of 29.36%, setting a new world record.
Implications for the Future of Solar Energy
The development of perovskite-CIGS tandem solar cells is a game-changer for the renewable energy sector. By significantly improving efficiency, these cells allow solar panels to generate more energy while occupying less space. This could lead to the production of smaller, lighter, and more affordable solar panels, making renewable energy accessible to a wider range of households and businesses worldwide.
One of the most significant challenges with perovskite technology has been its rapid degradation. However, the advancements in crystallinity and impurity reduction have addressed this issue, enhancing the durability and commercial viability of perovskite-based solar cells.
As governments and industries around the globe seek clean and efficient energy solutions, this new technology could play a pivotal role in accelerating the transition to renewable energy. If further advancements are made, perovskite-CIGS tandem cells could potentially dominate the photovoltaic market, reducing reliance on traditional silicon-based solar panels and lowering the cost of solar energy.
A New Era for Renewable Energy
The achievement of 29.36% efficiency with the 4T perovskite-CIGS tandem solar cell marks a significant milestone in solar technology. Once considered an “impossible material,” perovskite has now emerged as a cornerstone of renewable energy innovation. This breakthrough not only underscores the potential of perovskite but also highlights the importance of continued research and development in the quest for sustainable energy solutions.
As the world grapples with the urgent need to combat climate change, advancements like these offer a glimmer of hope. The future of solar energy is brighter than ever, and perovskite is leading the charge.
To better understand the significance of the 29.36% efficiency achieved by the perovskite-CIGS tandem solar cells, it’s essential to benchmark this breakthrough against other leading solar technologies. Traditional silicon-based solar cells, which dominate the market, typically achieve efficiencies ranging from 15% to 22%, with the highest laboratory records reaching around 26%. These cells, while reliable and widely adopted, are limited by their reliance on bulky, rigid materials and high manufacturing costs. Emerging perovskite-silicon tandem cells have pushed this boundary further, achieving efficiencies of up to 40% in experimental settings, but they still face challenges related to scalability and long-term stability. Meanwhile, standalone CIGS (copper-indium-gallium-selenide) solar cells generally operate at efficiencies between 18% and 23%, offering advantages in flexibility and lightweight design but falling short in terms of peak performance. The new 4T perovskite-CIGS tandem cell not only surpasses these figures but also combines the lightweight, flexible advantages of CIGS with the superior light absorption properties of perovskite. This positions the technology as a strong contender for applications where both high efficiency and adaptability are critical, such as in urban environments, portable energy solutions, or even space exploration. By bridging the gap between performance and practicality, the perovskite-CIGS tandem cell sets itself apart as a transformative advancement in the competitive landscape of renewable energy solutions, offering a compelling alternative to traditional and emerging technologies alike.
Related Content
- Biophotovoltaic Systems: The Next Evolution in Solar Energy
- Mercedes-Benz Revolutionizes Electric Vehicles with Solar Paint
- Space-Based Solar Power: A Revolutionary Leap in Energy Production
- A Comprehensive Look at Two Innovative Renewable Energy Projects: Solar Highways and the Western Green Energy Hub
- MIT Develops Battery-Free Solar Desalination System: A Game-Changer for Clean Water Access
- Harnessing the Sun: The Imperative Shift to Solar Energy for a Sustainable Future
- Scientists achieve world-record feat on quest for low-cost power supply: ‘Much higher efficiencies’
- Perovskite/CIGS tandem solar cells: progressive advances from technical perspectives – ScienceDirect
- HZB Sets New World Record for CIGS Perovskite Tandem Solar Cells – Helmholtz-Zentrum Berlin (HZB)