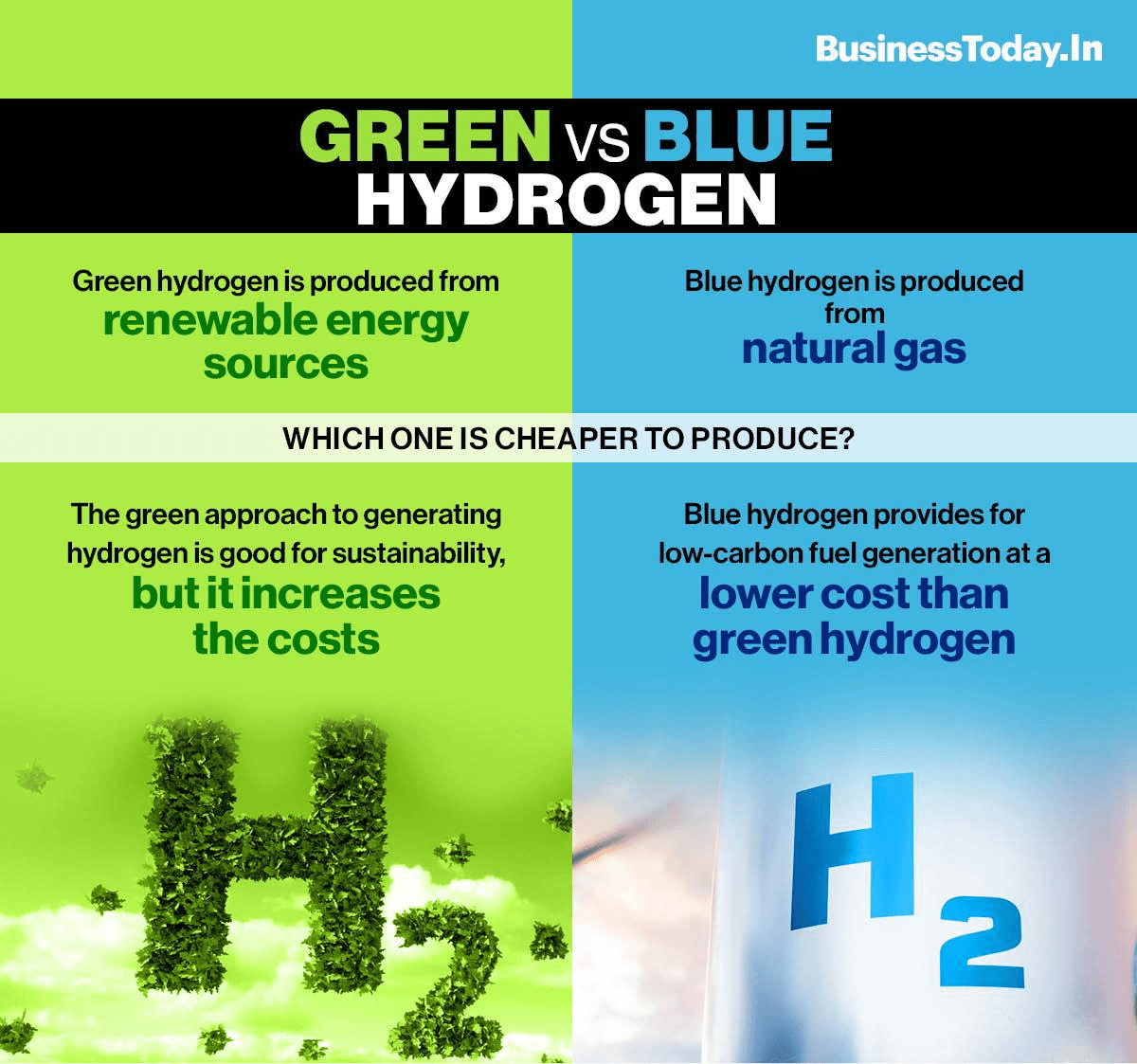
Blue Hydrogen: A Clean Energy Dilemma
Despite being touted as a cleaner alternative to traditional fossil fuels, blue hydrogen faces significant environmental challenges. The production process, which involves carbon capture and storage (CCS), can lead to methane leakage, energy-intensive CCS operations, and potential CO2 storage leaks. These factors undermine the notion of blue hydrogen as a truly clean energy source, raising concerns about its contribution to climate change.