The renewable energy landscape is witnessing a revolutionary development: biophotovoltaic (BPV) systems that harness the power of cyanobacteria to convert solar energy into electricity. This groundbreaking technology, spearheaded by German researchers, represents a potential paradigm shift in how we think about solar power generation. By utilizing the natural process of photosynthesis combined with electron-capturing mechanisms, these systems offer a unique approach to sustainable energy production.
Current Technology Overview
The Power of Cyanobacteria
At the heart of this innovation lies Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803, a species of cyanobacteria with remarkable capabilities. These microscopic organisms perform a sophisticated form of photosynthesis that not only captures CO2 but also generates electrons that can be harvested for electricity production. The process employs ferricyanide as a mediator to facilitate electron transfer to electrodes, creating a living solar cell.
Key Advantages Over Traditional Solar
The advantages of BPV systems extend far beyond conventional solar technology. These bacterial systems possess the unique ability to self-repair and adapt to environmental changes, actively removing CO2 from the atmosphere while generating power. Their versatile operation allows for functioning in varied light conditions, potentially extending power generation beyond peak sunlight hours. Furthermore, the biological approach requires fewer rare earth materials compared to traditional solar panel manufacturing, reducing the environmental impact of production.
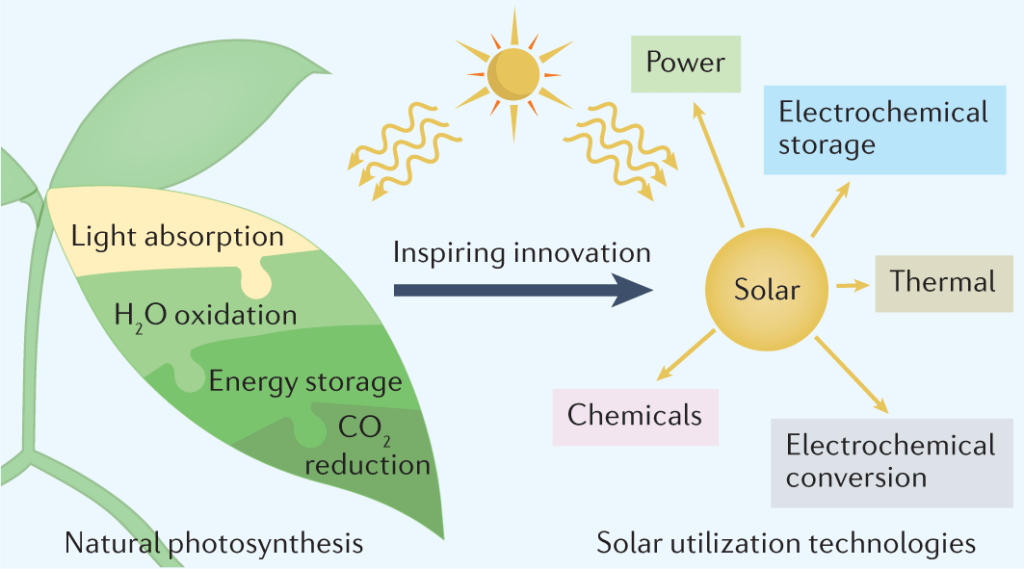
Future Developments and Possibilities
Near-Term Innovations (2025-2030)
The immediate future of BPV technology focuses on efficiency improvements through genetic engineering techniques that optimize electron production and transfer efficiency. Researchers are developing advanced mediator compounds that may surpass ferricyanide’s capabilities, while also exploring biofilm engineering for improved electron collection. Integration with existing infrastructure remains a priority, with hybrid systems combining BPV with traditional solar installations showing particular promise.
Medium-Term Prospects (2030-2040)
As the technology matures, we anticipate seeing BPV systems incorporated into building materials and city infrastructure. Agricultural applications may emerge, combining power generation with crop production in innovative ways. Marine applications could see floating BPV platforms utilizing seawater and marine cyanobacteria, while self-sustaining systems with automated maintenance optimize bacterial growth conditions.
Long-Term Possibilities (2040-2050)
Looking further ahead, large-scale BPV farms could significantly impact atmospheric CO2 levels through widespread deployment. Bio-computing integration might combine power generation with biological computing capabilities, while space applications could see modified BPV systems generating power on other planets. The development of synthetic ecosystems could optimize energy production while providing additional environmental benefits.
Technical Challenges and Solutions
The primary challenges facing BPV technology include current efficiency rates, which achieve only a fraction of traditional solar panel efficiency, and scalability issues in maintaining optimal conditions for bacterial growth. System stability needs improvement for commercial viability, while initial setup and maintenance costs require optimization.
Emerging solutions incorporate artificial intelligence for real-time monitoring of bacterial health and automated optimization of growth conditions. Advanced materials research focuses on new electrode materials and improved containment systems, while biological enhancements through CRISPR-based genetic modifications and synthetic biology approaches create more optimal strains.
Environmental and Economic Impact
BPV systems offer significant environmental benefits through active carbon sequestration during power generation and reduced manufacturing waste compared to traditional solar panels. The technology provides potential water purification benefits and features biodegradable components that reduce end-of-life waste.
From an economic perspective, while initial research and development costs remain high, the potential for reduced maintenance costs due to self-repair capabilities presents a compelling long-term advantage. The technology creates new opportunities in biotechnology and renewable energy sectors, potentially establishing entirely new markets for bio-based energy systems.
Implementation Strategies
Implementation begins with pilot projects in controlled environments, focusing on data collection and system optimization while building public awareness. Commercial deployment follows, integrating with existing renewable energy infrastructure and developing standardized production methods. Large-scale implementation will eventually see the construction of dedicated BPV farms and integration into smart city infrastructure, supported by global distribution networks.
In Short
Biophotovoltaic systems represent a promising frontier in renewable energy technology. While significant challenges remain, the potential benefits of this technology warrant continued investment and research. The combination of power generation with carbon capture could provide a valuable tool in addressing climate change while meeting growing energy demands. As research continues and efficiency improves, BPV systems could become an integral part of our renewable energy infrastructure, complementing existing technologies and providing new opportunities for sustainable development. The success of this technology could mark a significant step toward a more sustainable and environmentally conscious energy future.
Related Content
- Harnessing Radiation: The Revolutionary Potential of Cladosporium sphaerospermum
- Could 1.2% of the Sahara Desert Power the World? A Theoretical Solution to Global Energy Demand
- The Environmental Catastrophe of War: Understanding the Crisis in Gaza
- Solar Panels on the Alps: Switzerland’s Bold Gamble with Nature
- Cool Roofs Are Best at Beating Cities’ Heat
- The Future of Renewable Energy: Innovations and Challenges
- Renewable Fuel Source | Miscanthus clon illinois
- Biophotovoltaics: Recent advances and perspectives
- Bio-Photovoltaic Systems: Boosting Efficiency – Rinnovabili
- University of Cambridge – Biological Photovoltaics (BPV) | Department of Biochemistry
- The Development of Biophotovoltaic Systems

